Well done everyone 🙂
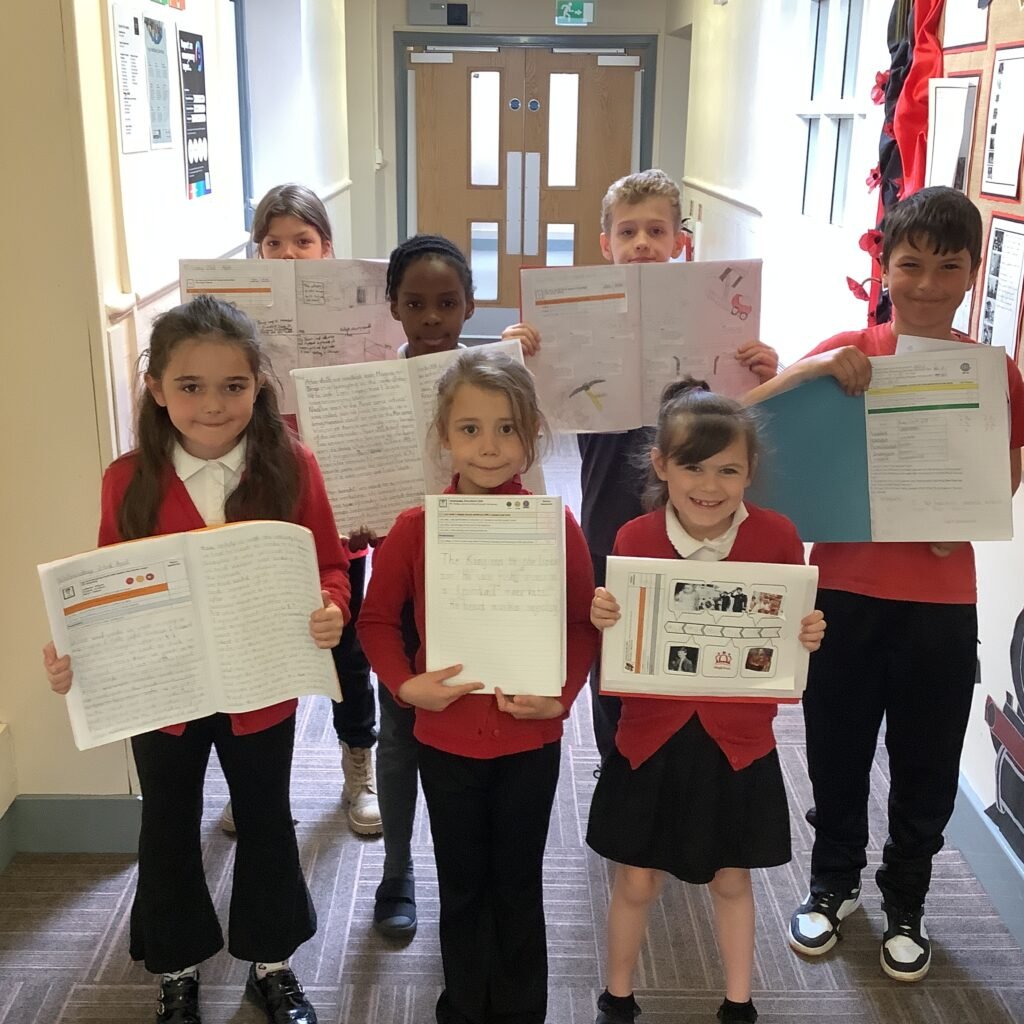

Well done everyone 🙂

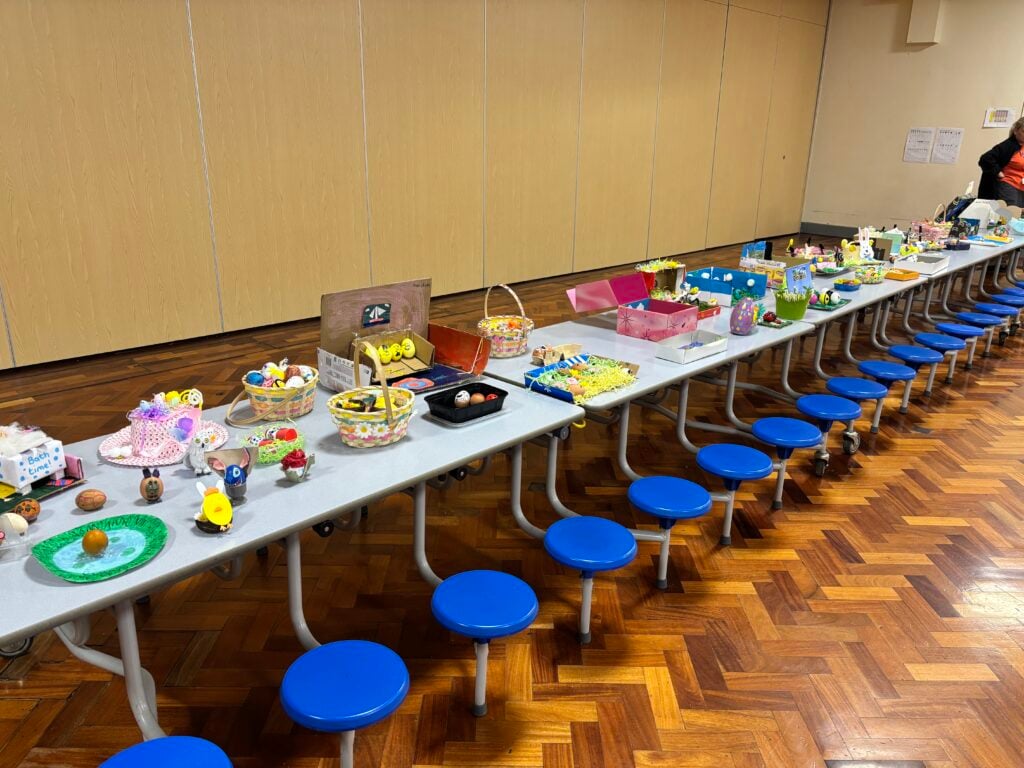
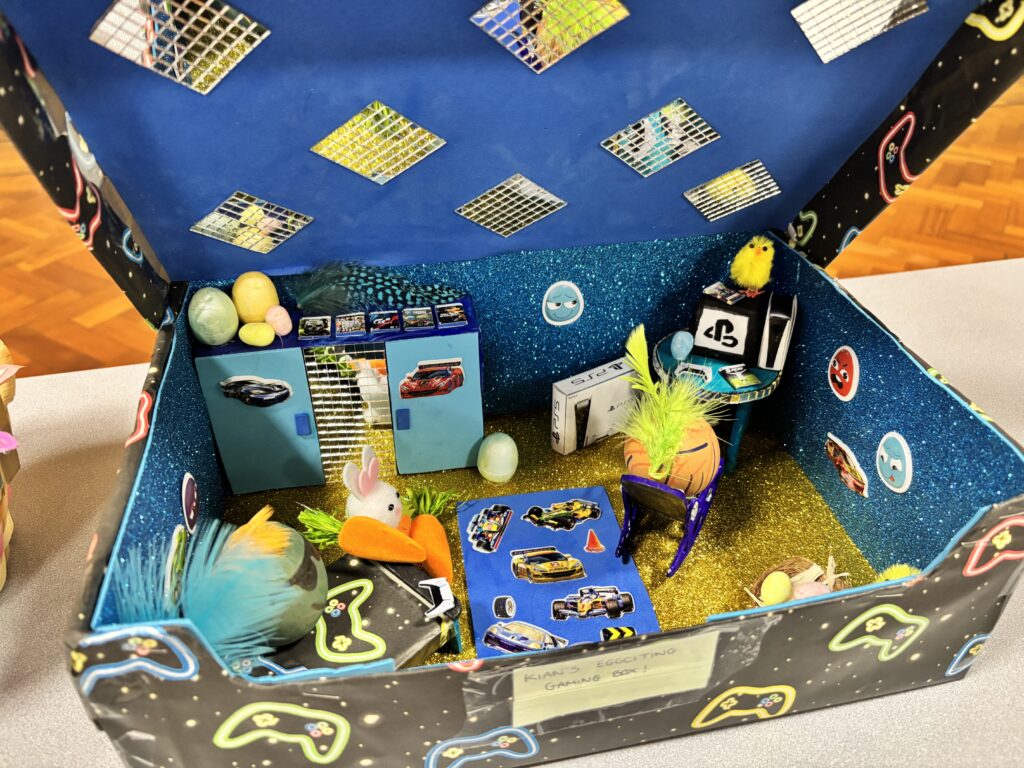
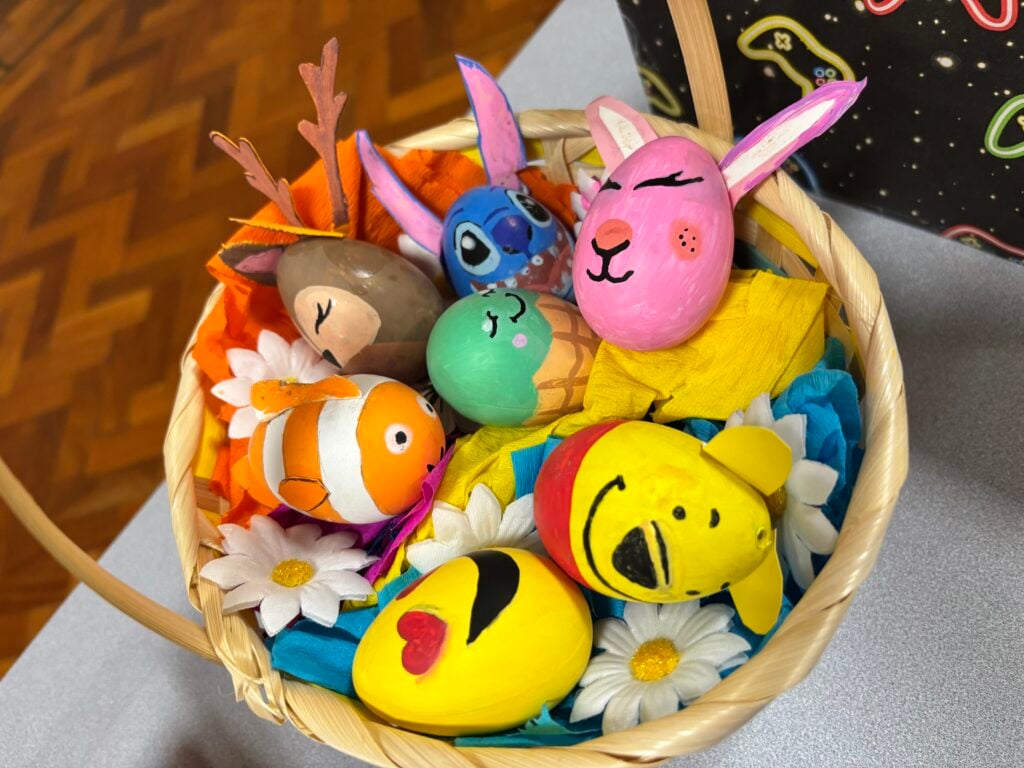
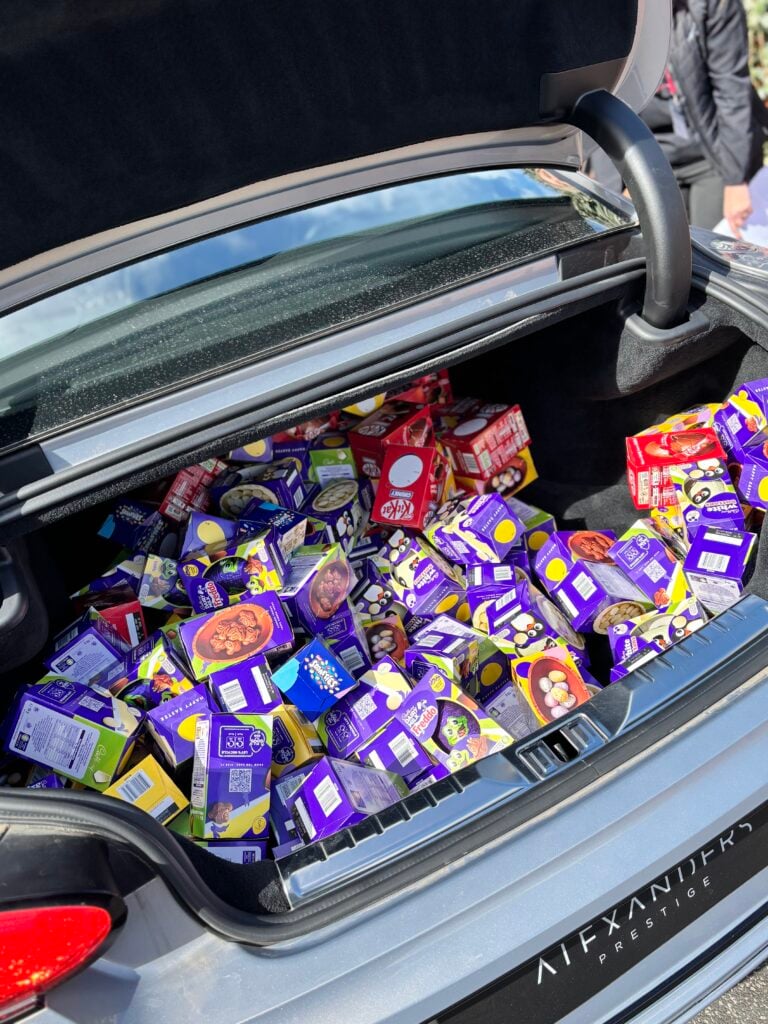
Crew Hamill’s amazing easter egg displays for the easter egg competition!!




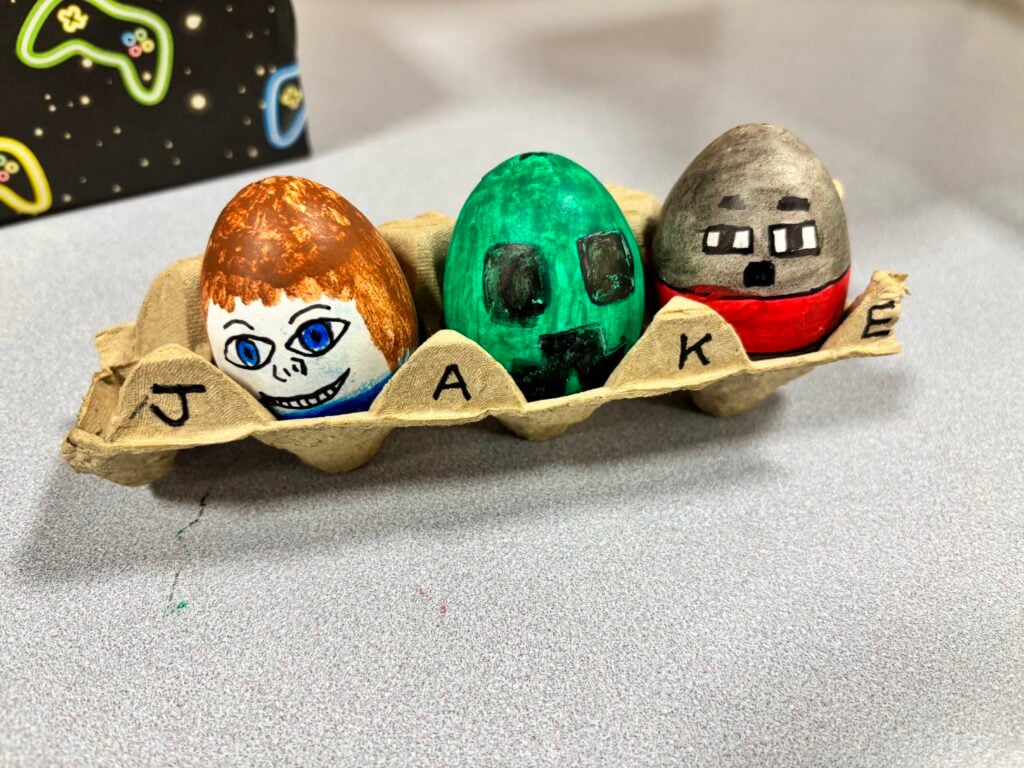

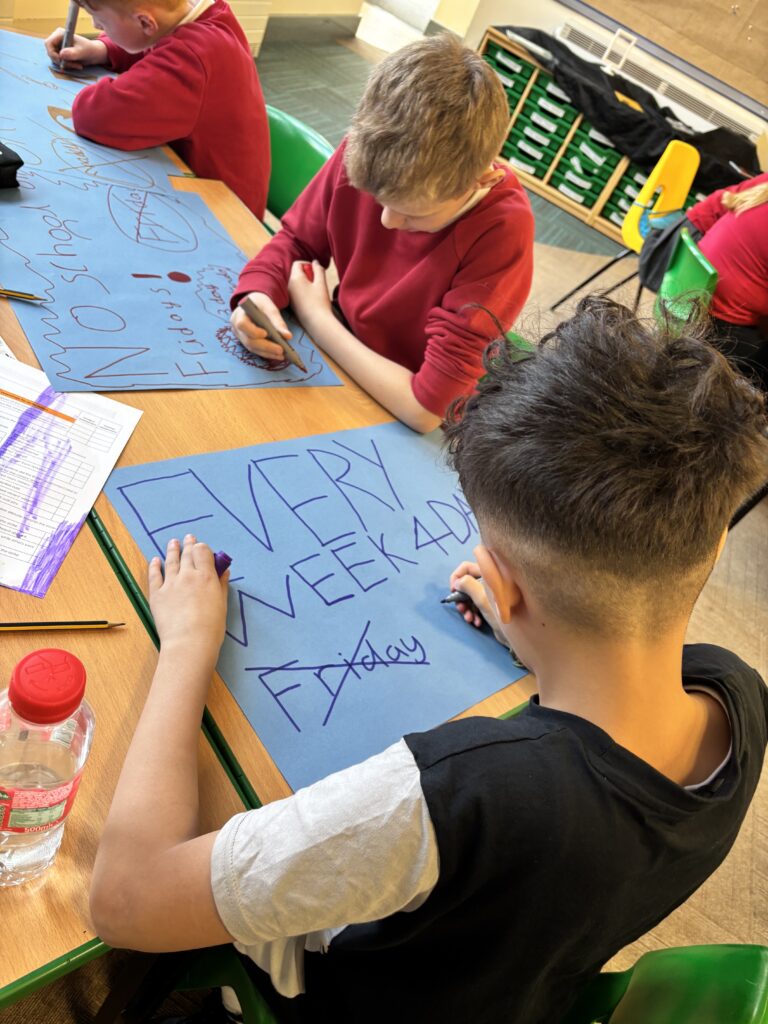
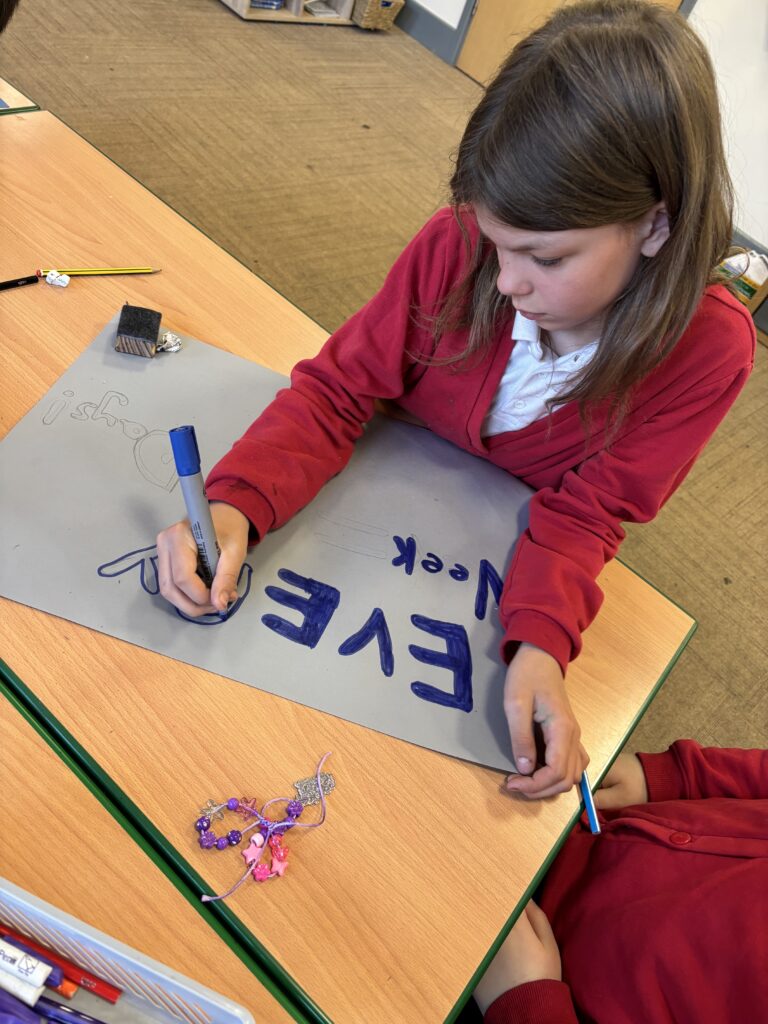
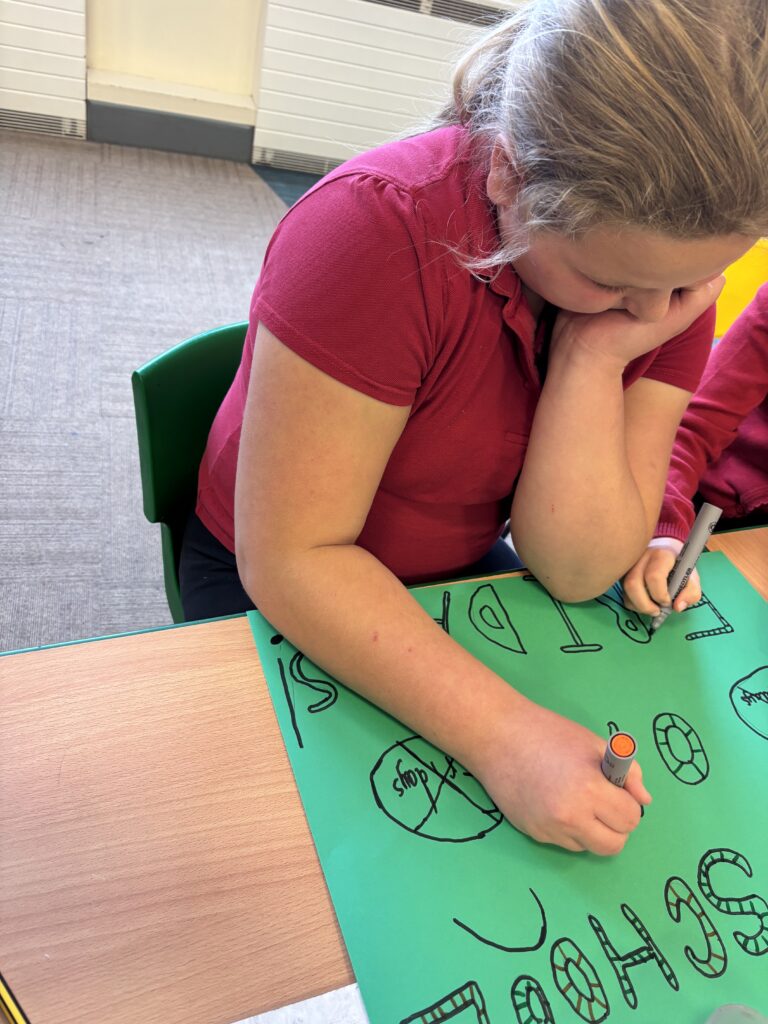
Crew Hamill and Crew Wilkinson had so much fun causing a little mischief on the streets of Carcroft whilst taking part in our very own strike. We showed a united front whilst fighting for what we believe in – a school with no uniform and a 4 day school week (no Fridays!!).
Thank you to everyone who cheered us on when they saw us and to those who gave us a beep of their horn!
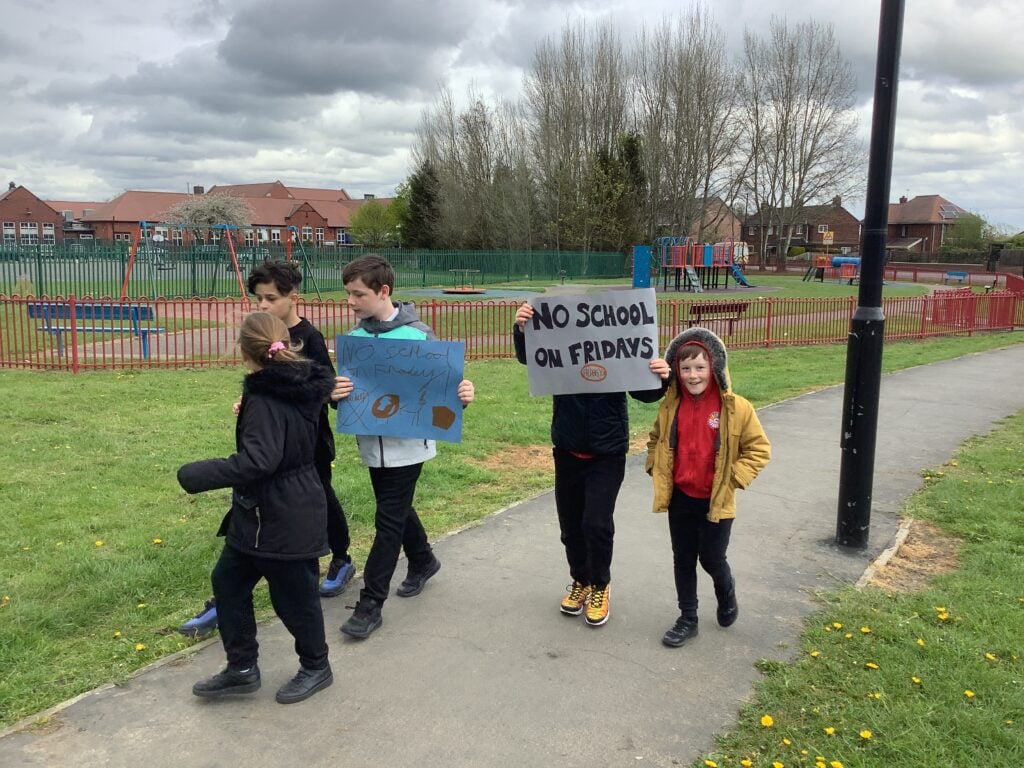
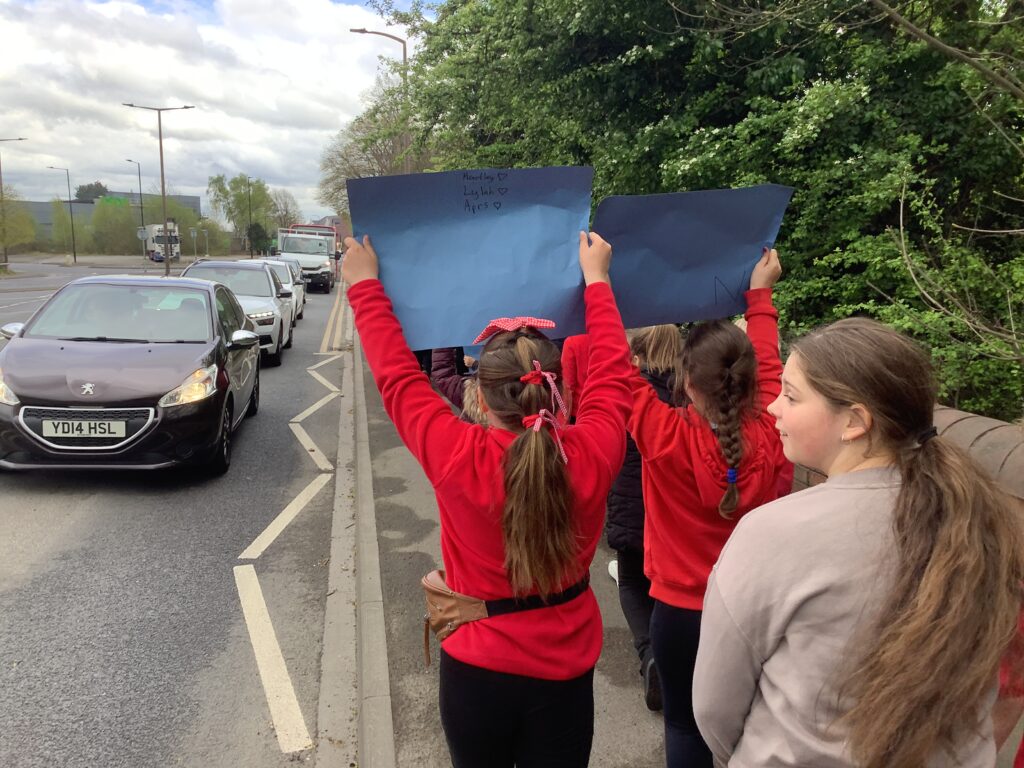
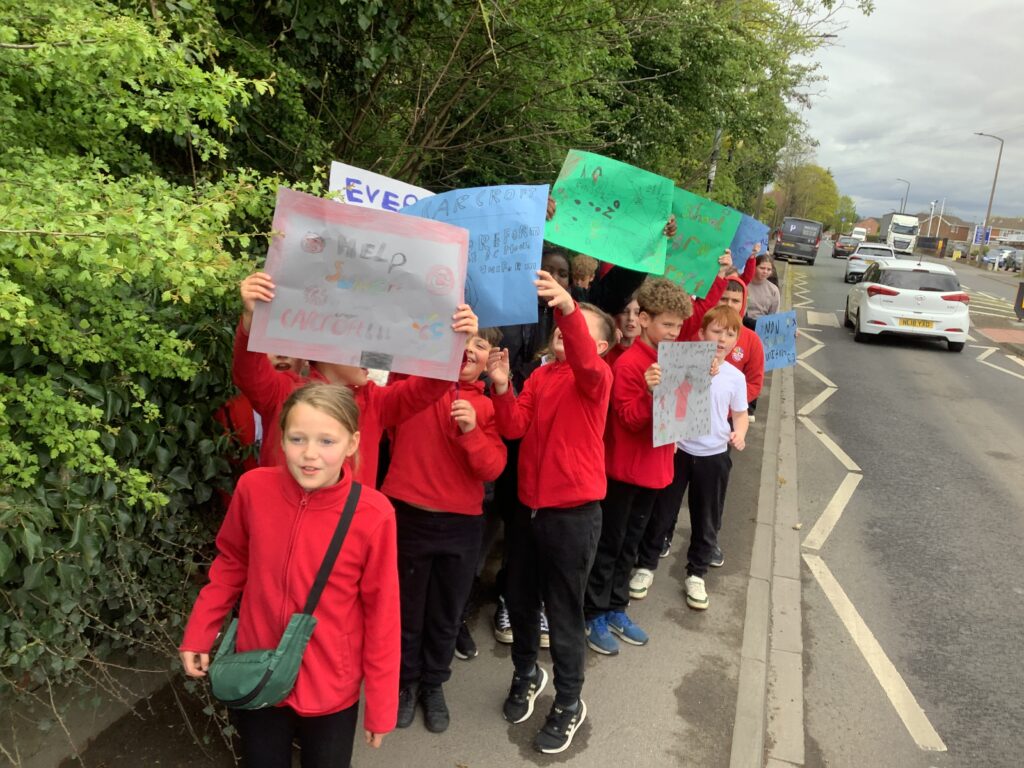
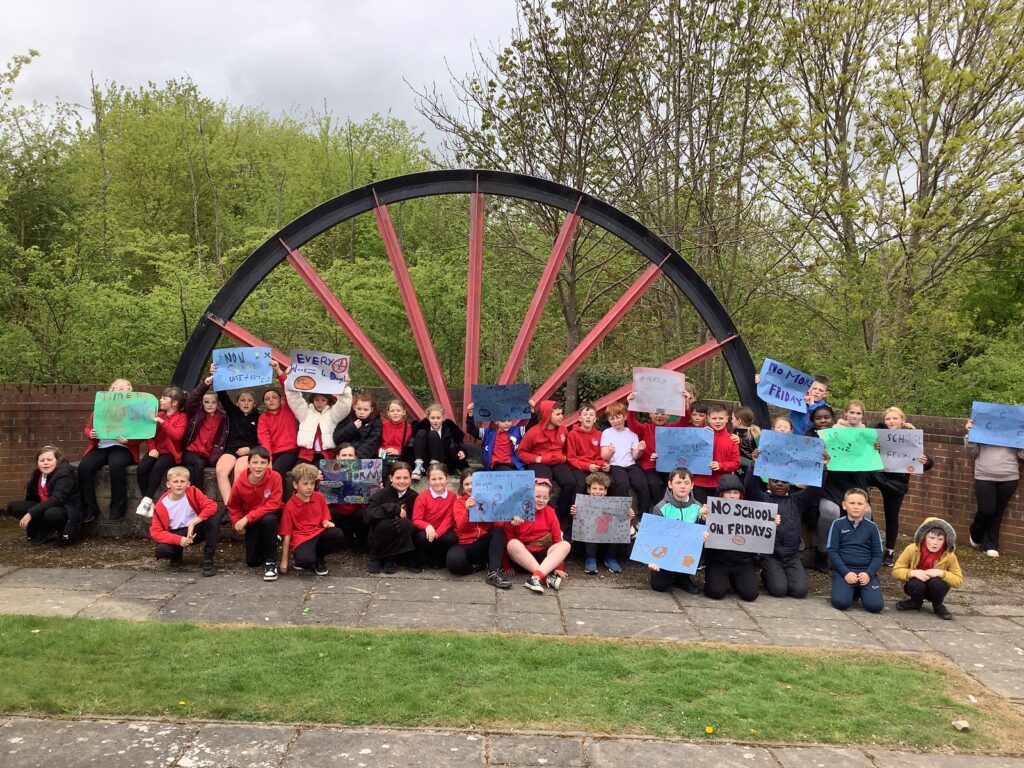
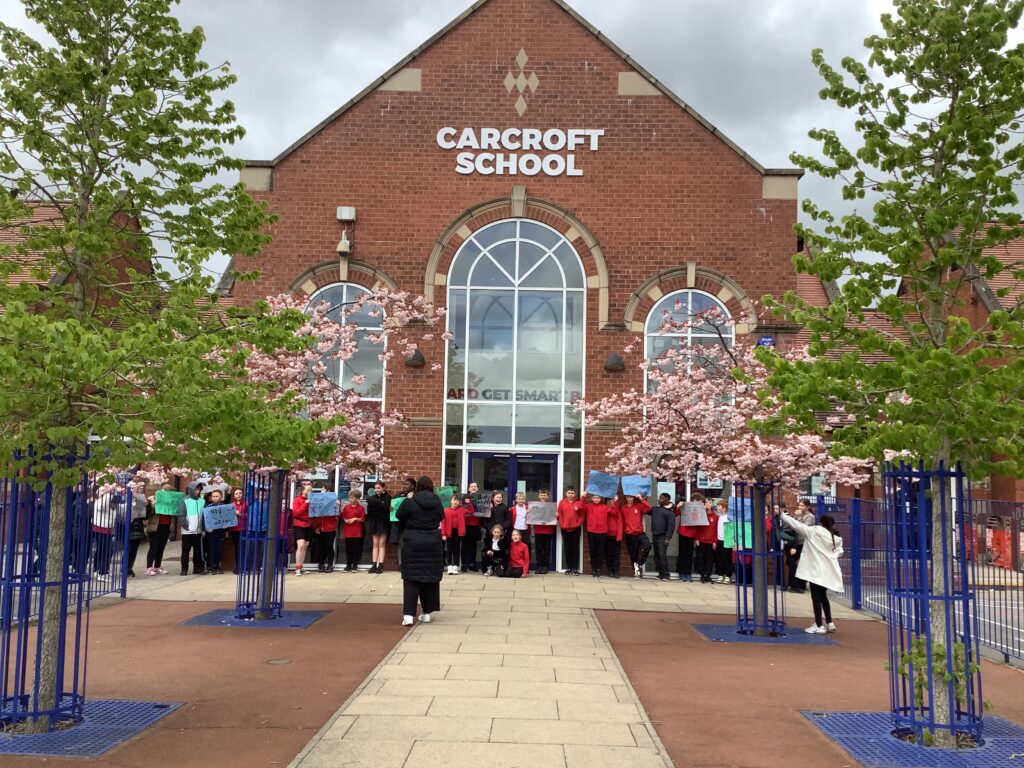
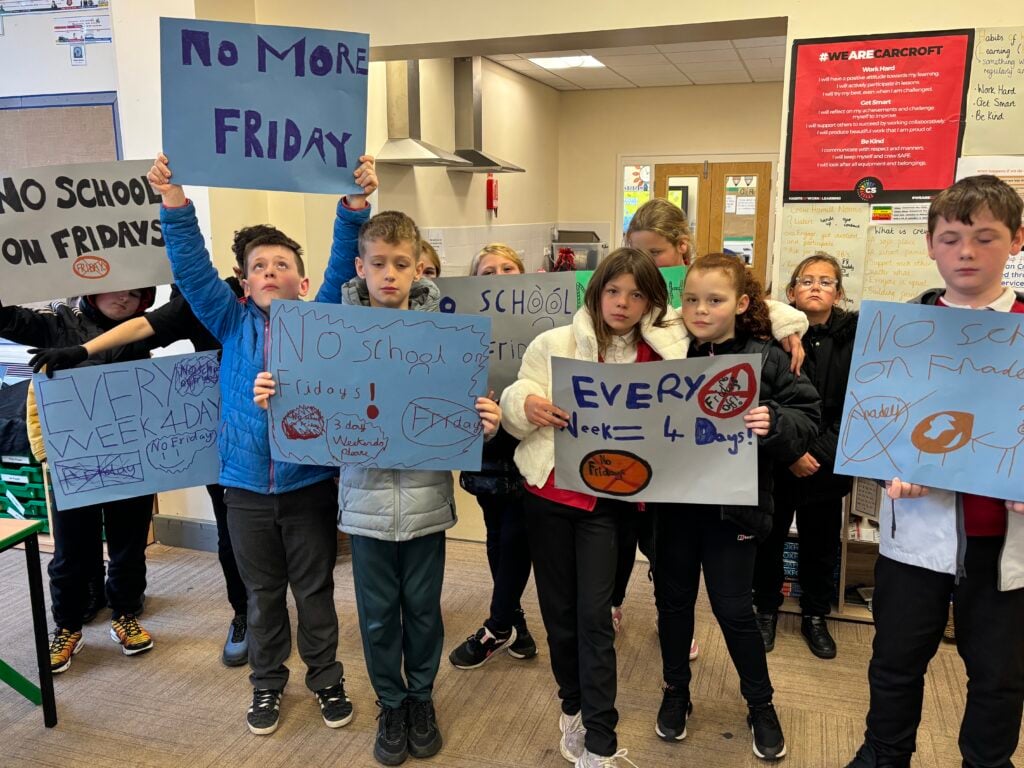
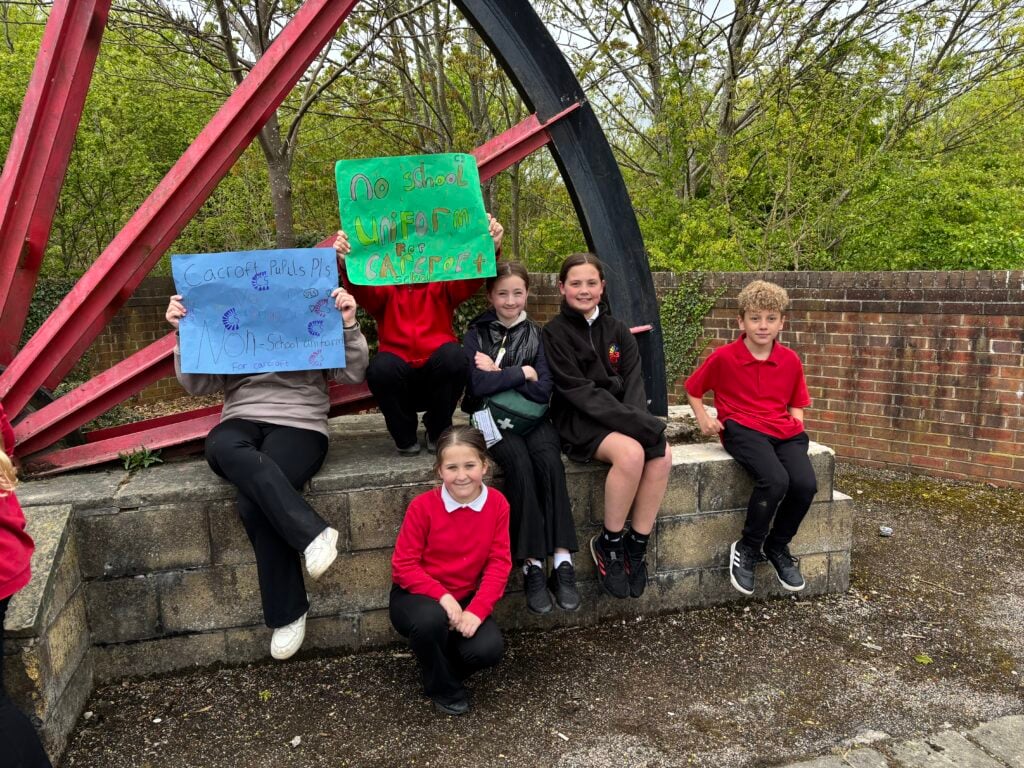
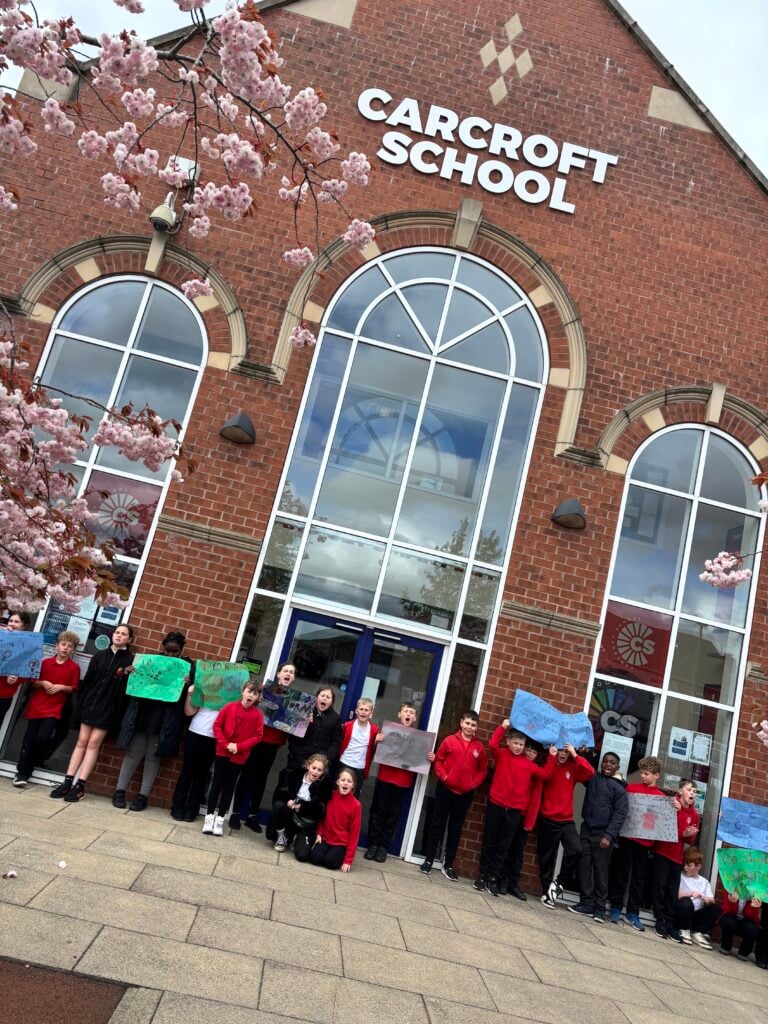
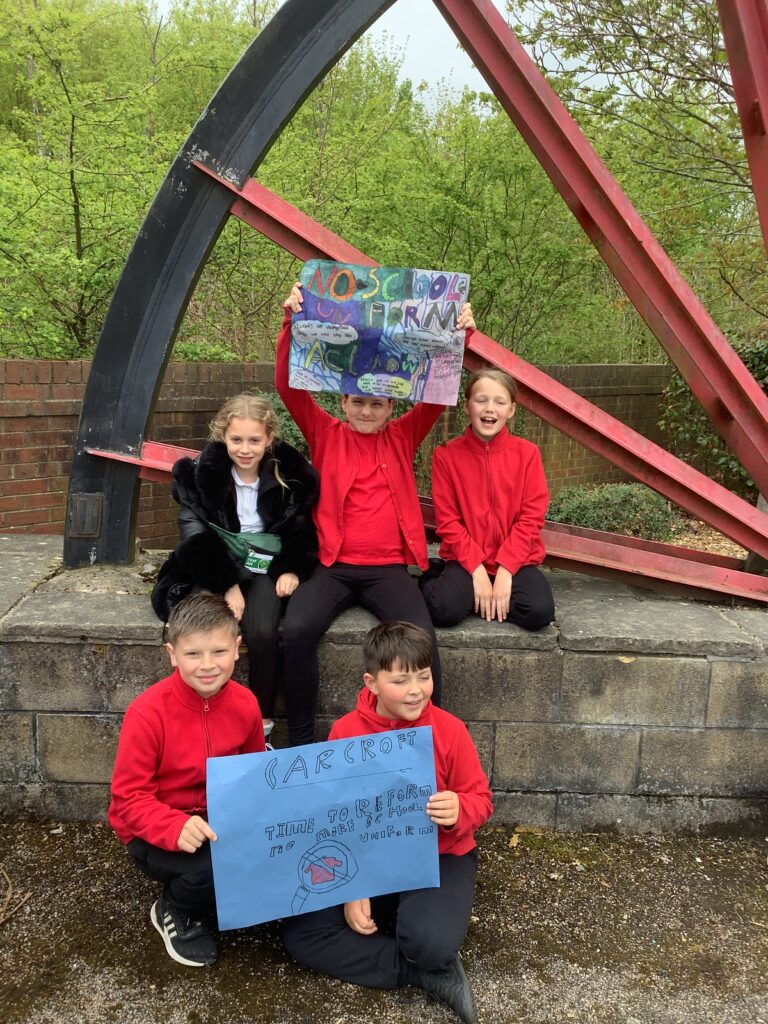










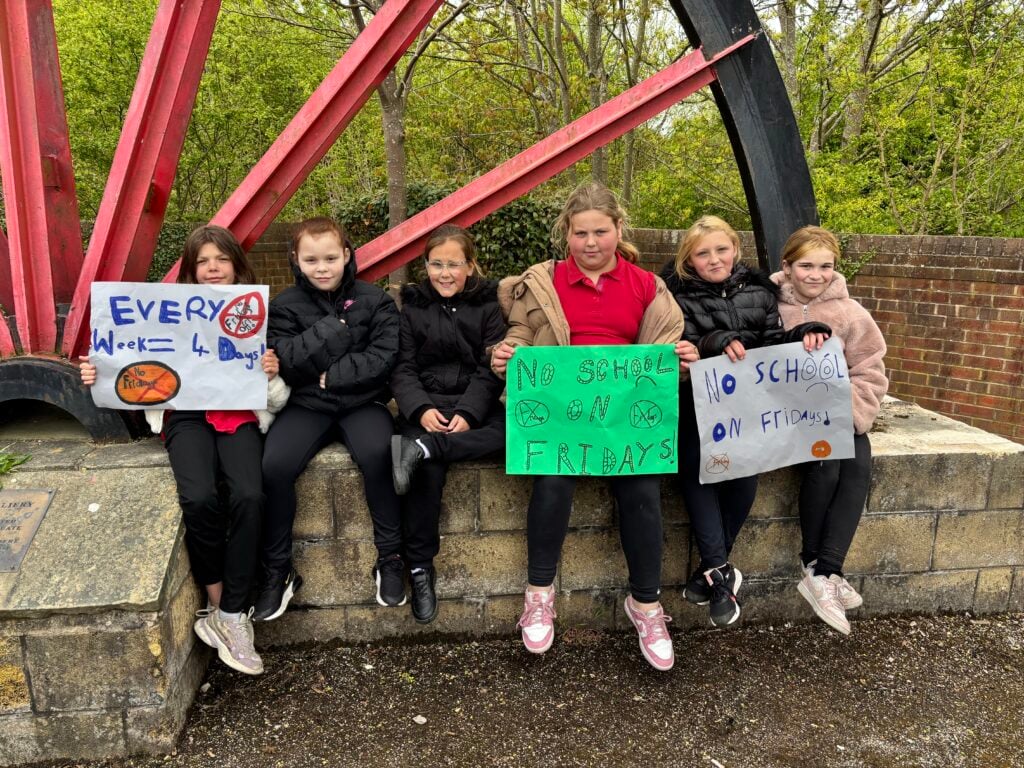



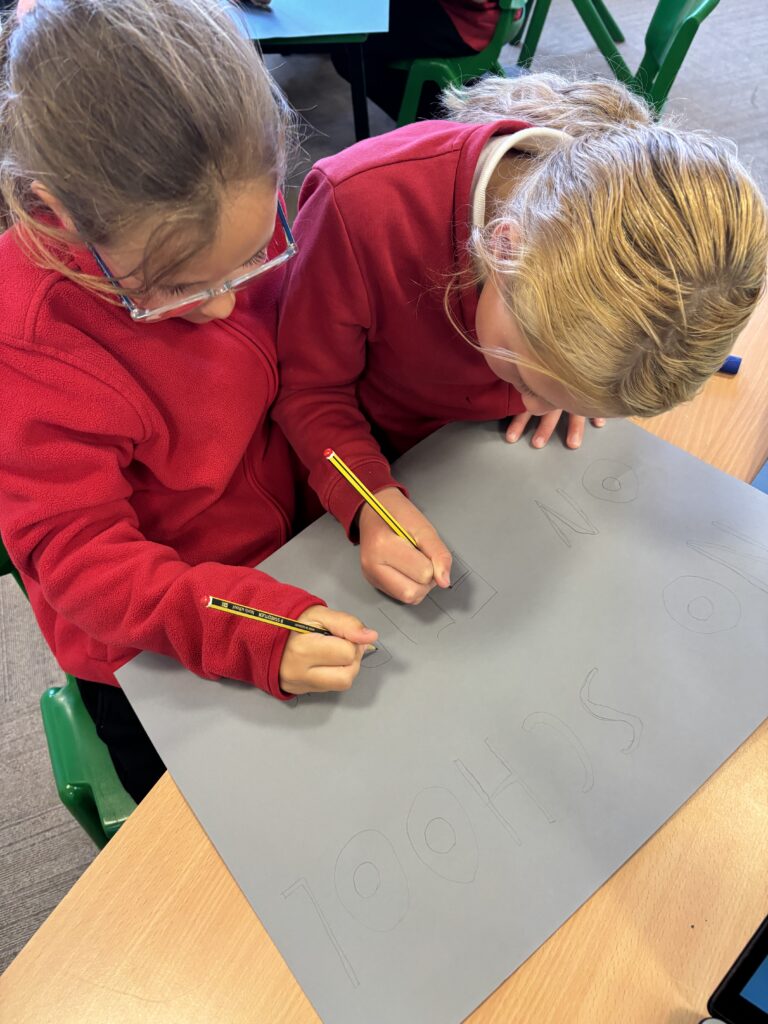
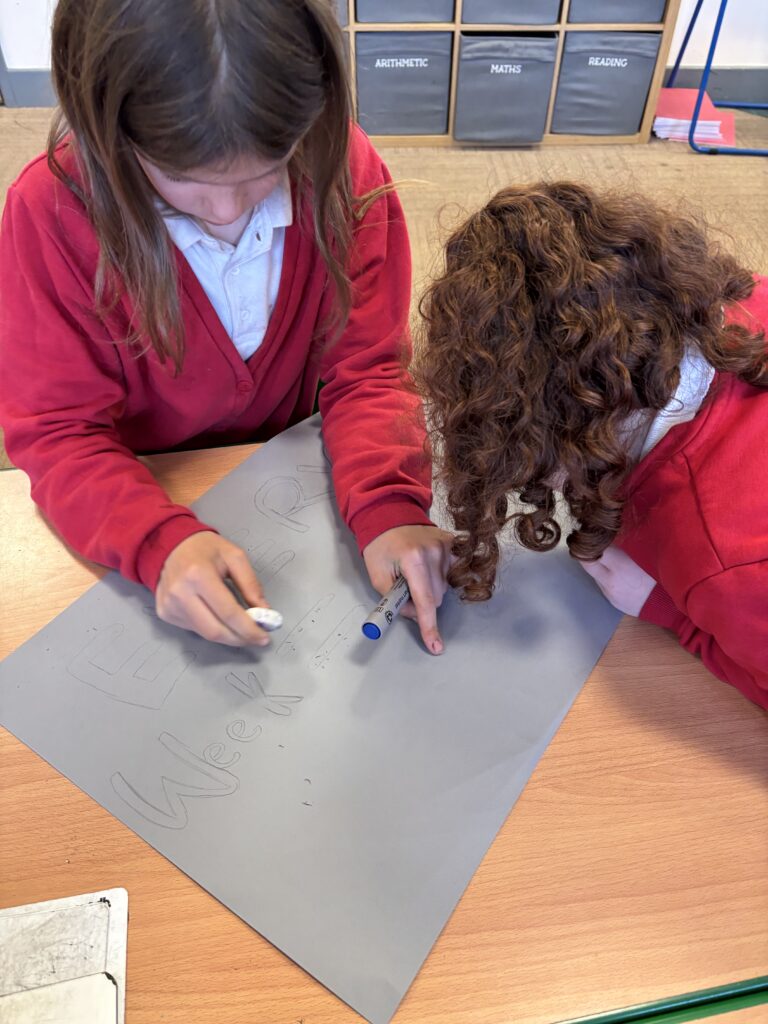
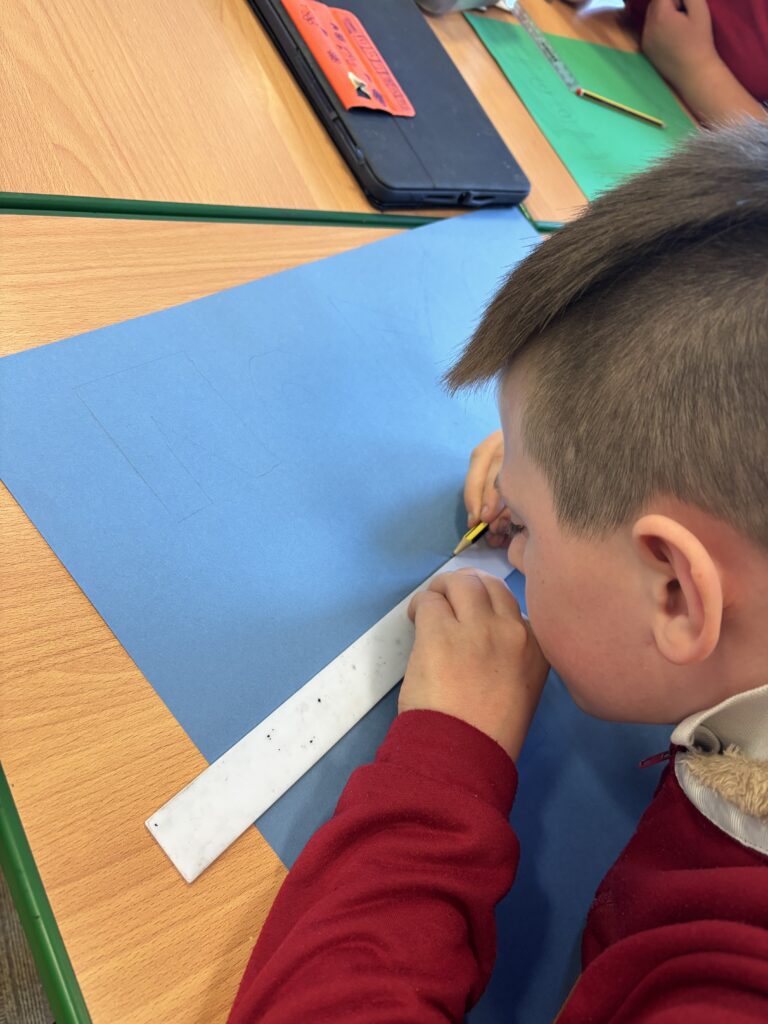
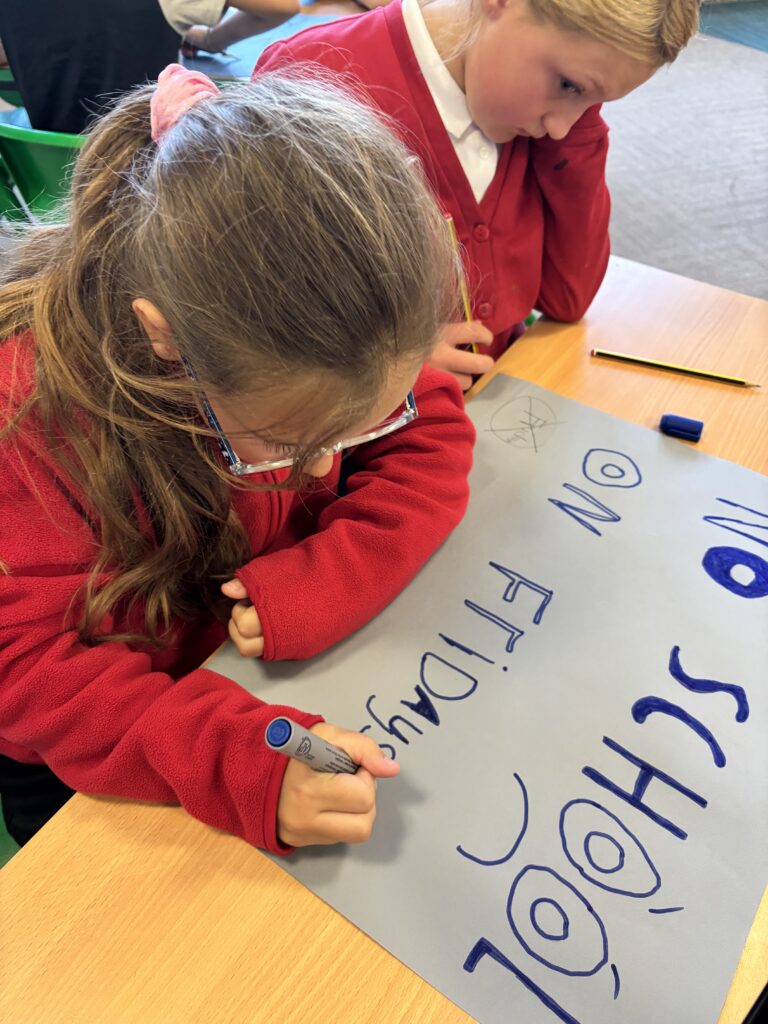
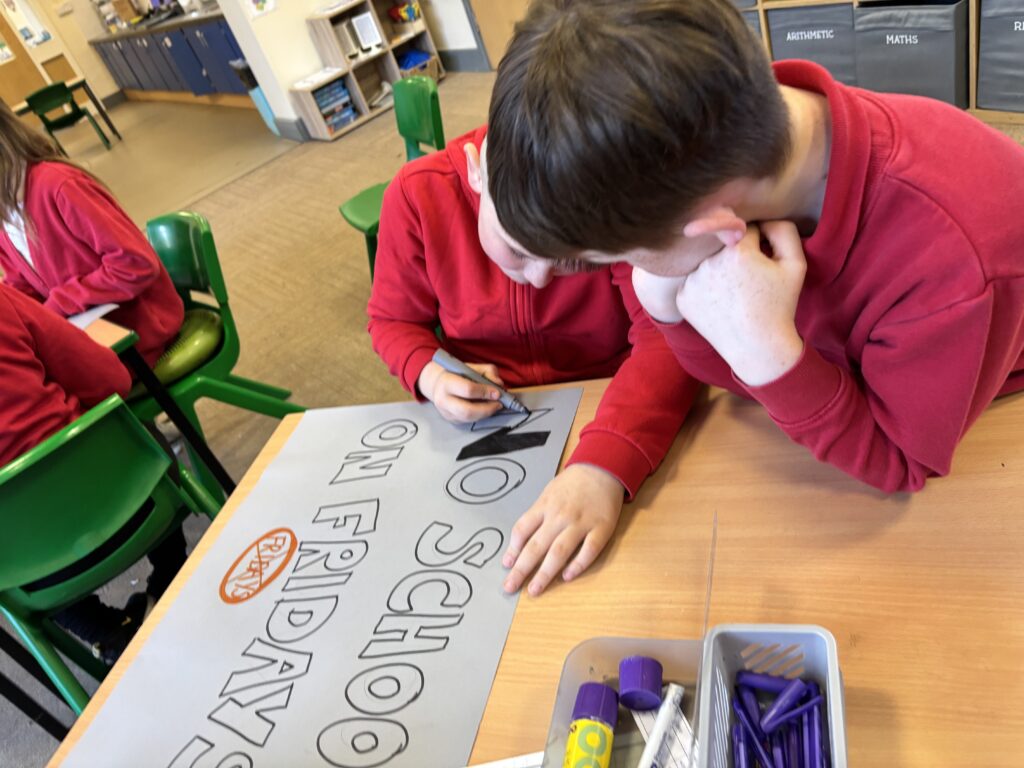
To hook us into our learning, we are going on STRIKE! Today, we have learnt all about the coal mine strikes and the reasonings as to why these took place. We were shocked to find out that 142,000 people actually went on strike when Margaret Thatcher tried to close 20 mines in 1984. Did you know that people who didn’t go on strike were called scabs?! Inspired by what we have learnt, we are planning our own strike! We have decided that the school week should always be a 4 day week and that we shouldn’t have to come to school on Fridays. This afternoon, we have designed and created placards which we are going to use when we go on strike later in the week. Keep your eyes peeled – we may just march past your house!









To kick start our new writing unit on poetry, Crew Hamill have looked at lots of different examples of poetry, including a video of poet Micheal Rosen reciting his famous poem ‘Chocolate Cake’ (this made us all laugh a lot!) and a video of some Roald Dahl poems that have been turned into songs. We then worked in pairs to identify as many different features of poetry as we could, include rhyme, rhythm, line breaks, stanzas and personification.






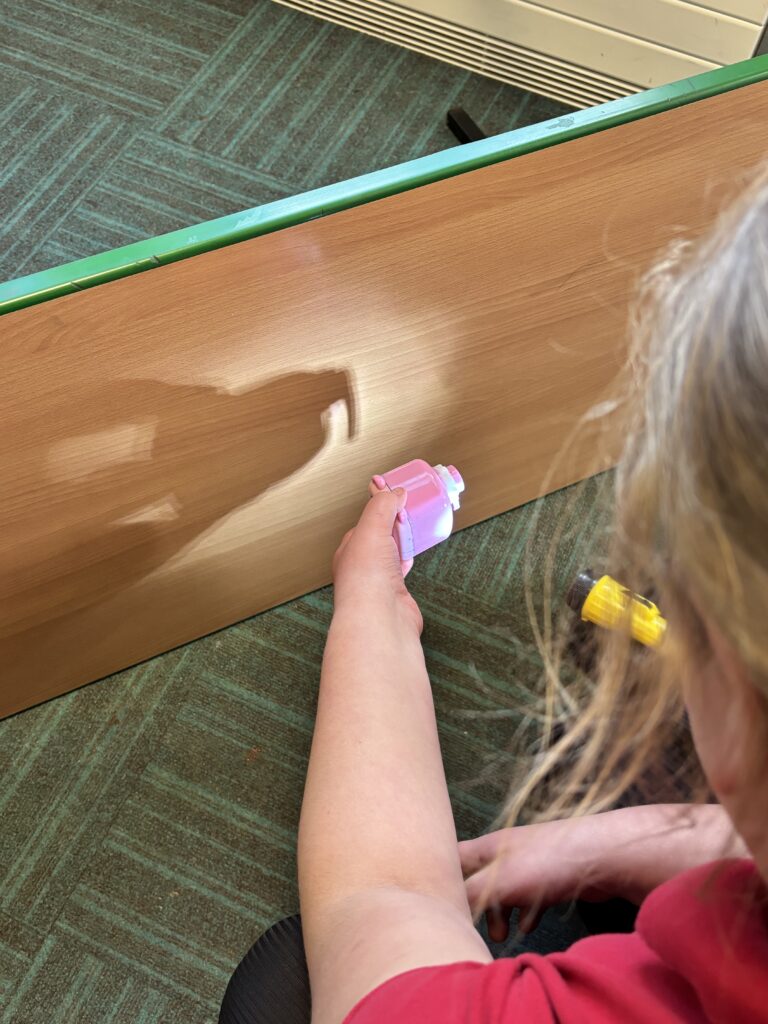
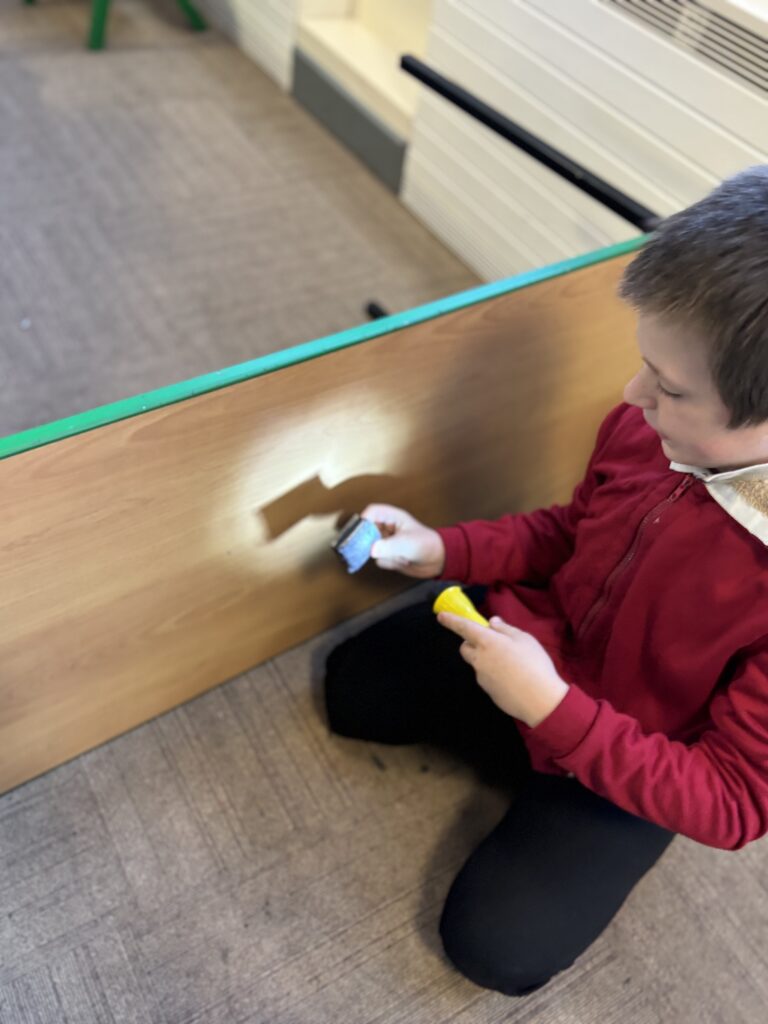
Crew Hamill spent time today exploring how shadows are formed. Once we’d worked out that shadows are formed by opaque objects blocking a light source, we experimented to see how we could change these shadows. We identified that when an object was closer to the light source, the shadow was larger as more of it was blocked and when the object was further away, the shadow was smaller as there was less of it being blocked.





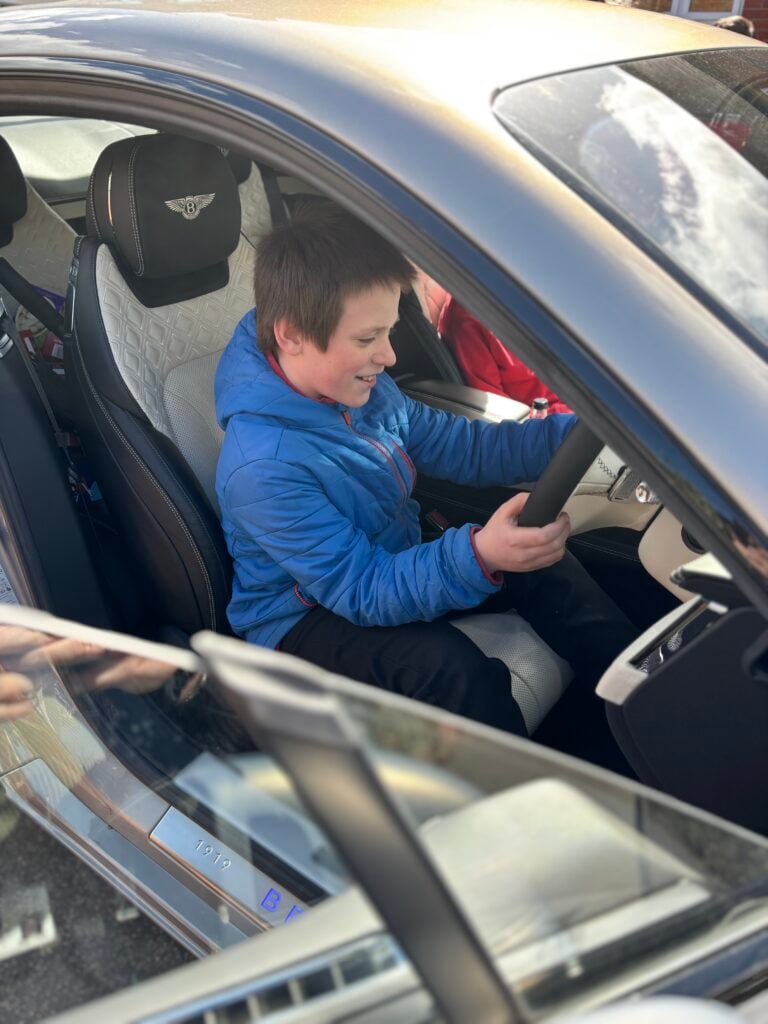
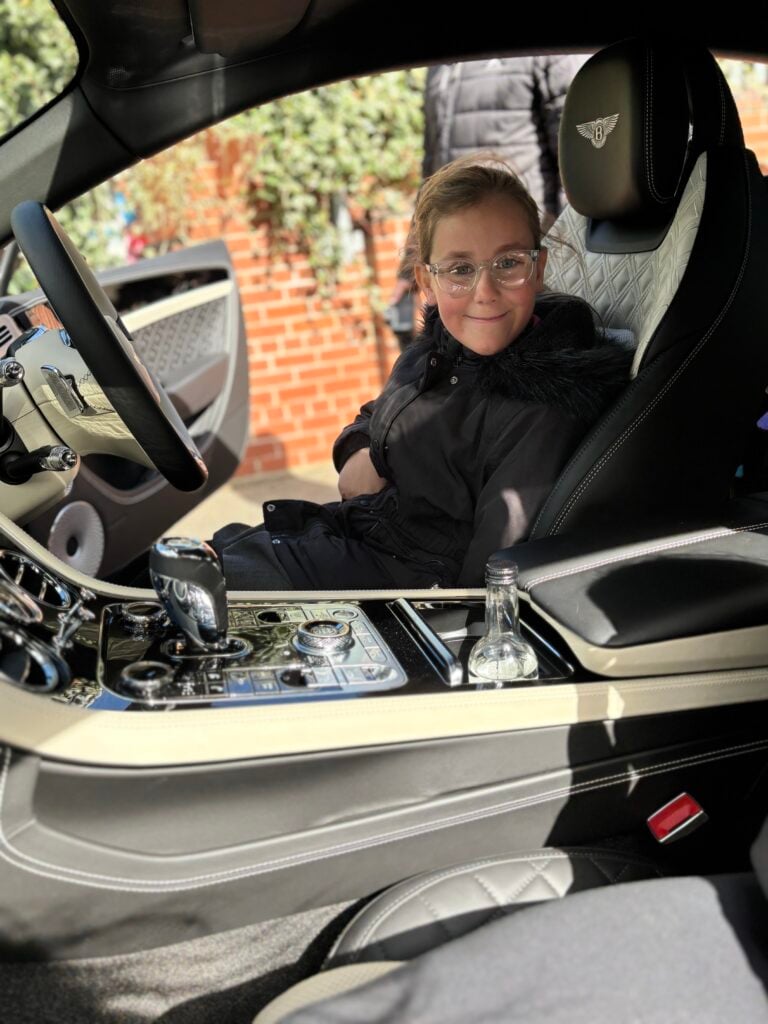
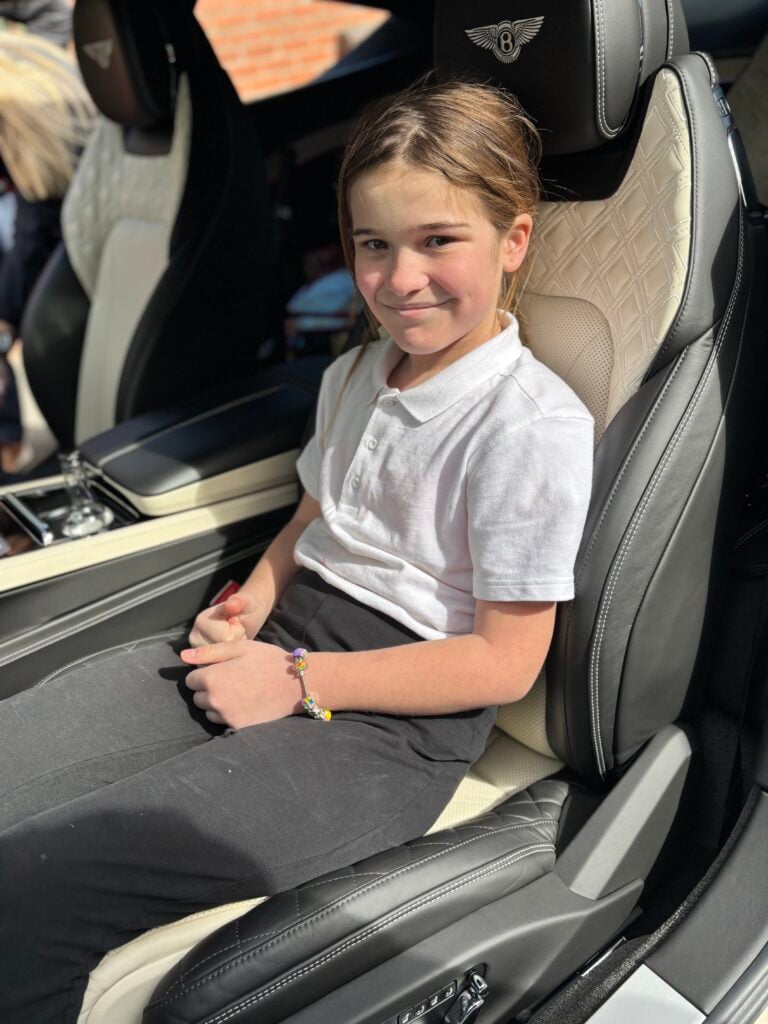
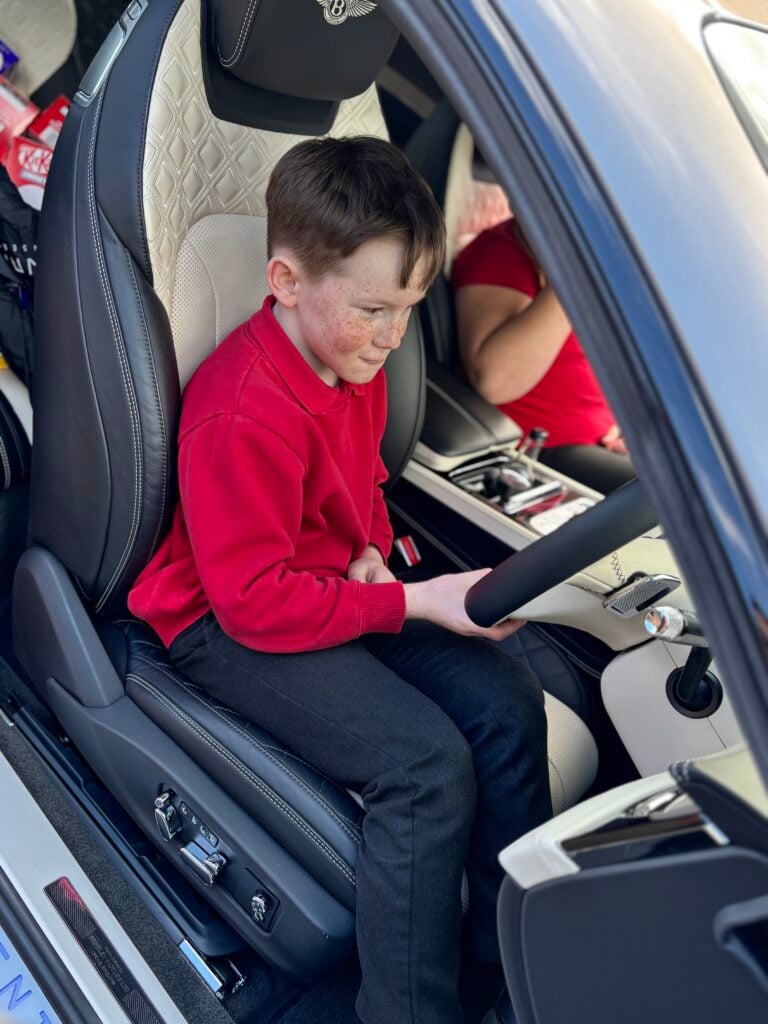
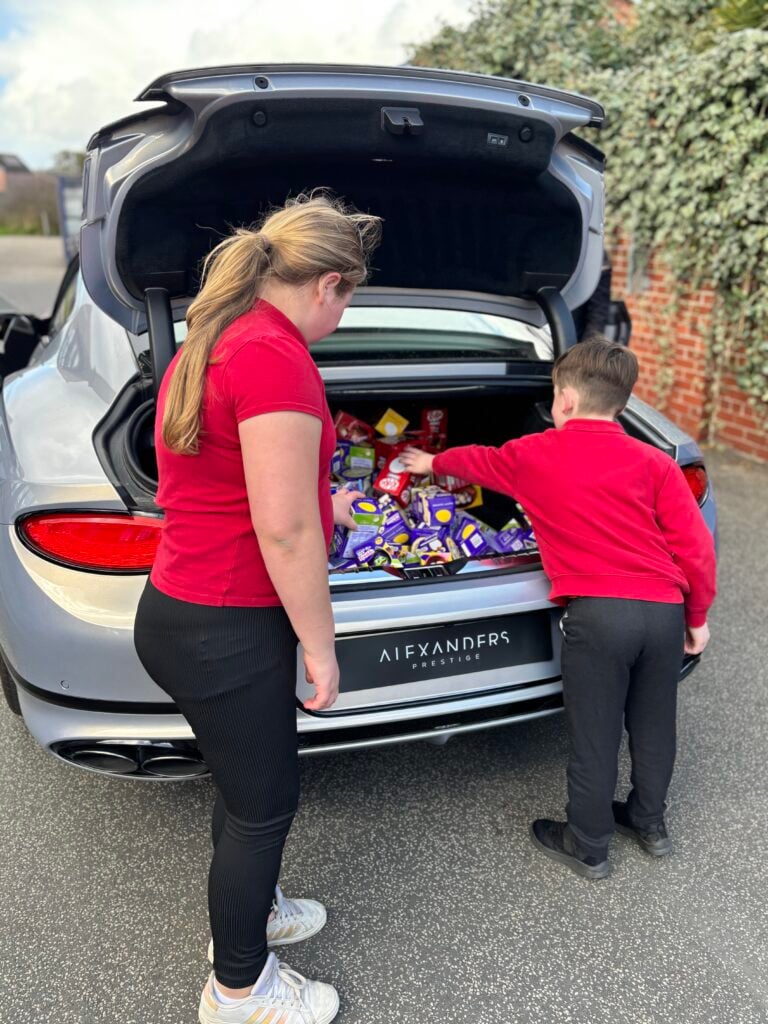
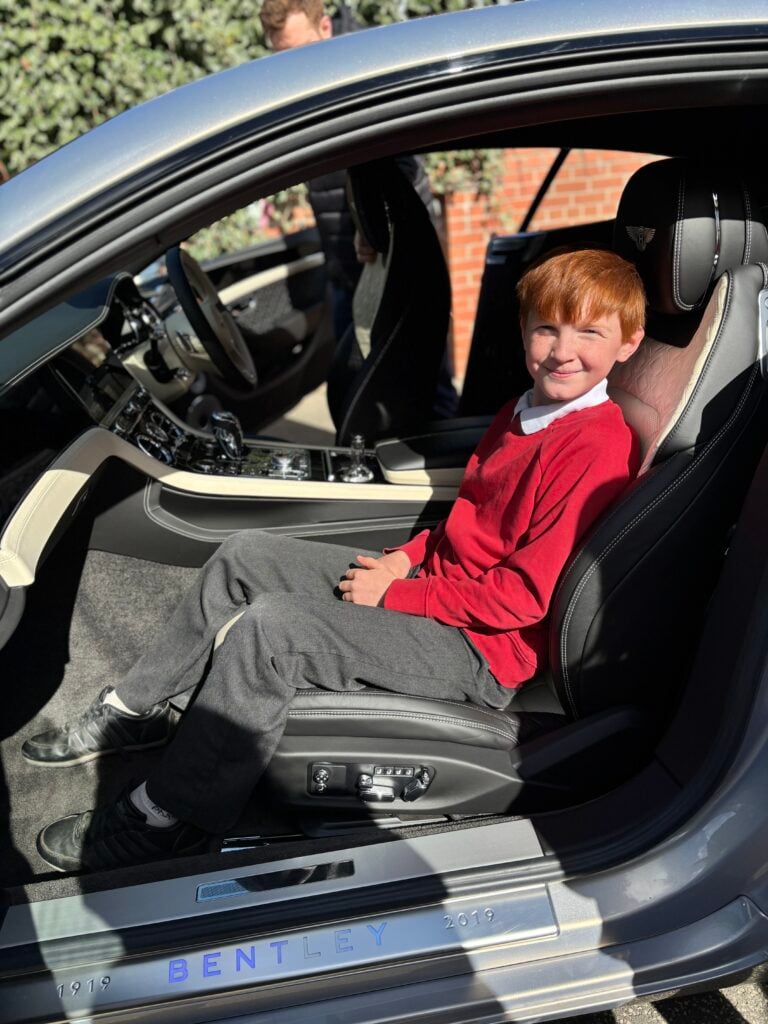
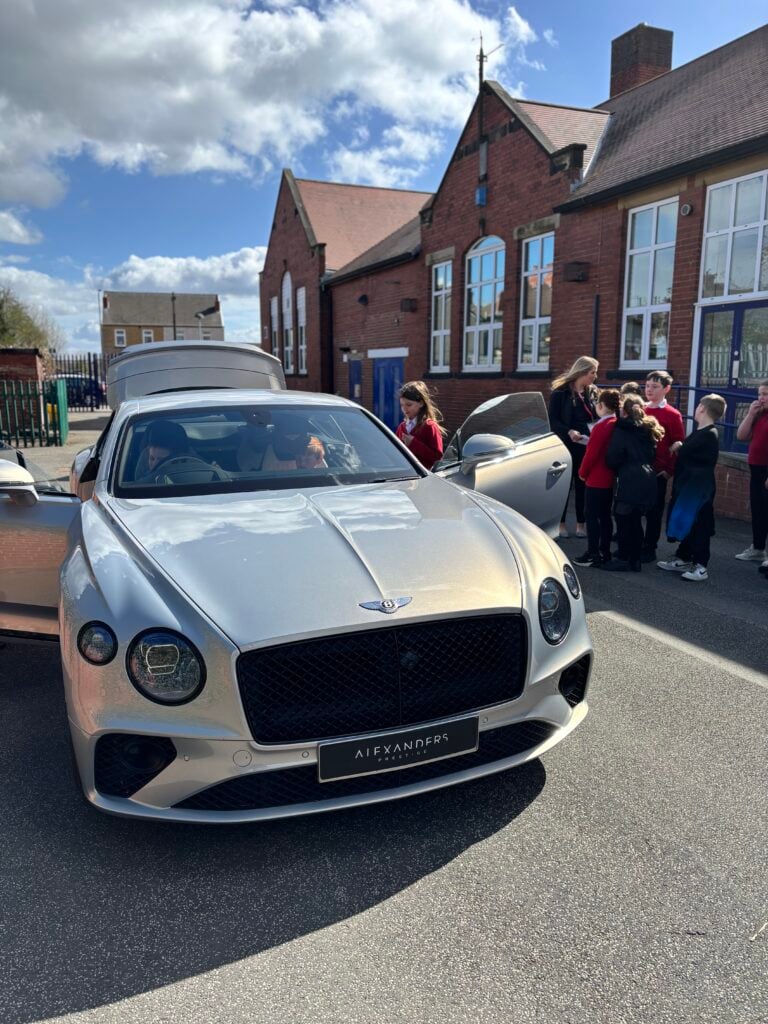
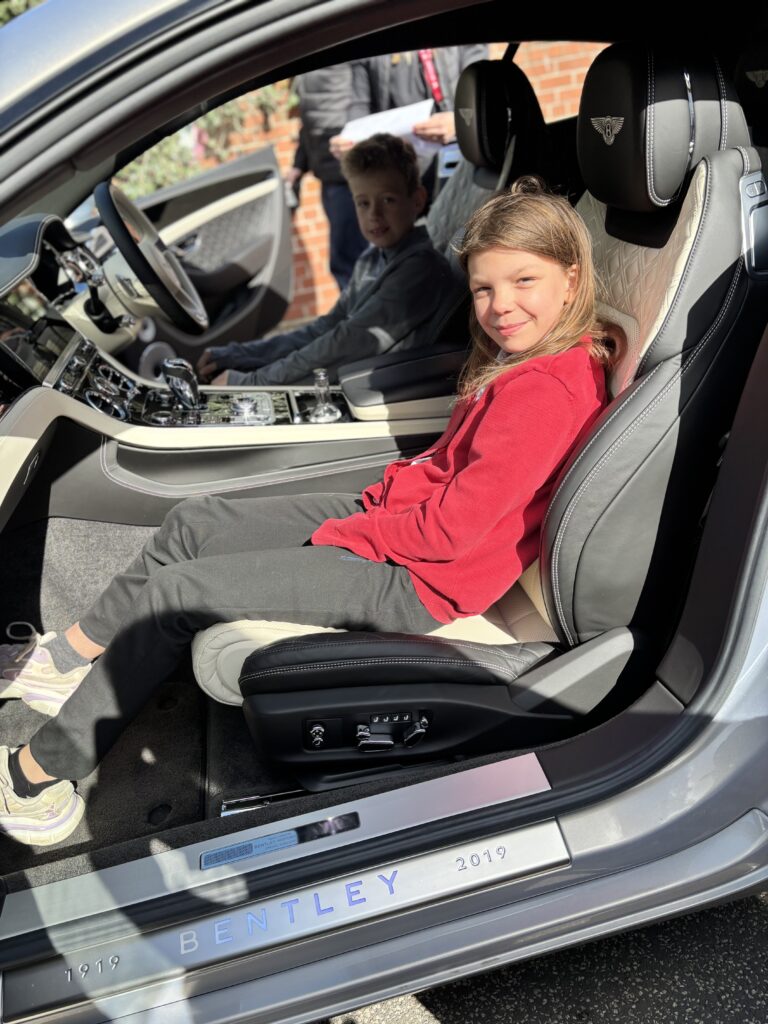
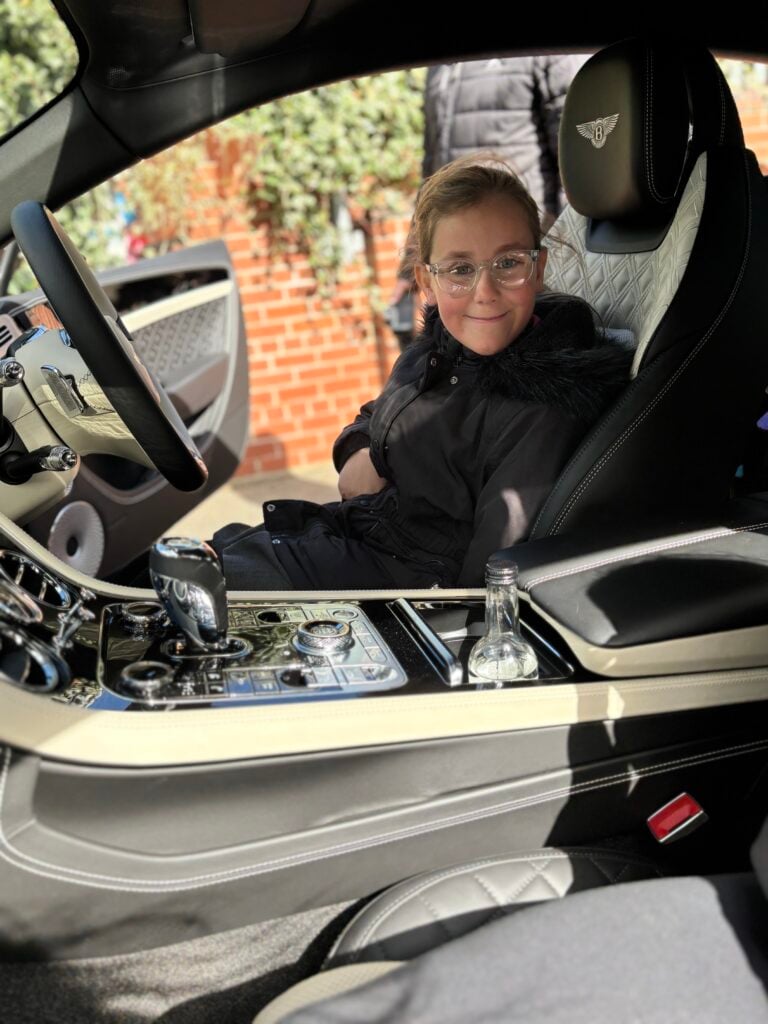
Crew Hamill have absolutely LOVED having the opportunity to take a seat in a super car today! The visitors were extremely kind and let each of us have the chance to sit in the front seat. Not only that, but they also brought each of us an easter egg!!











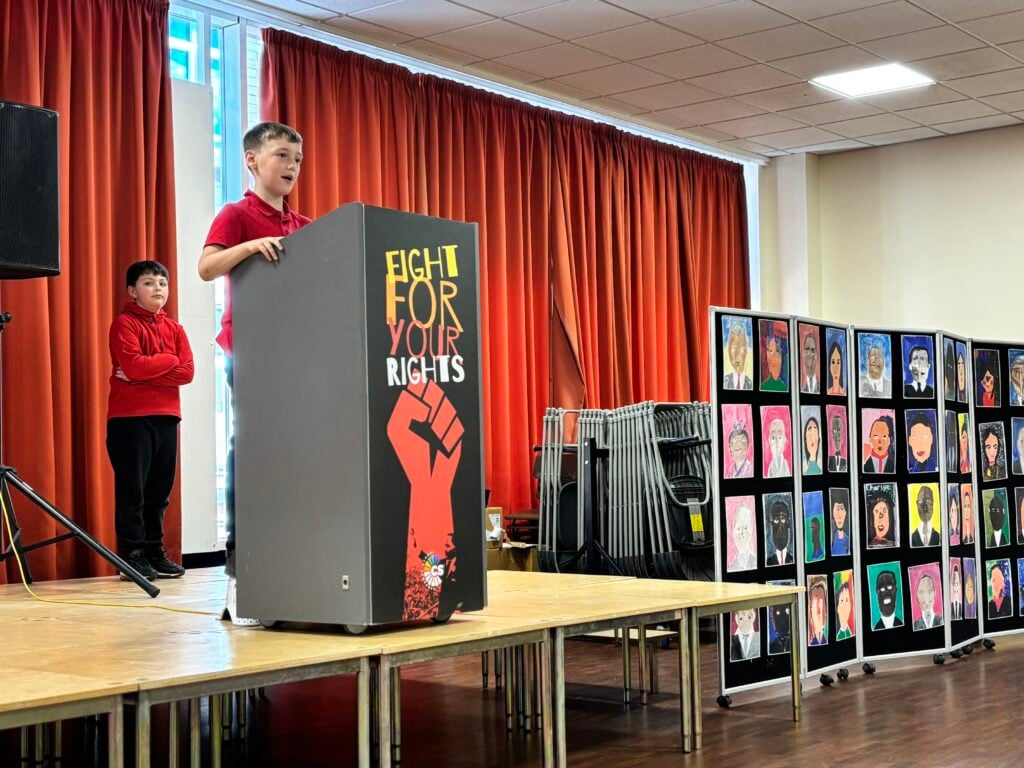
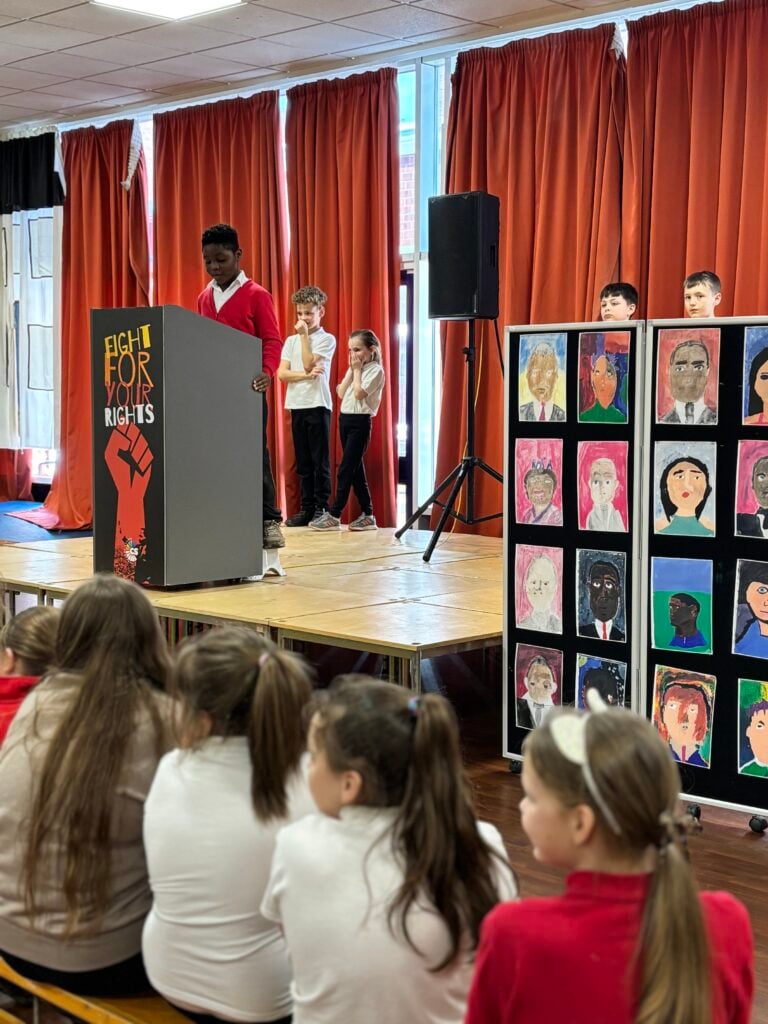
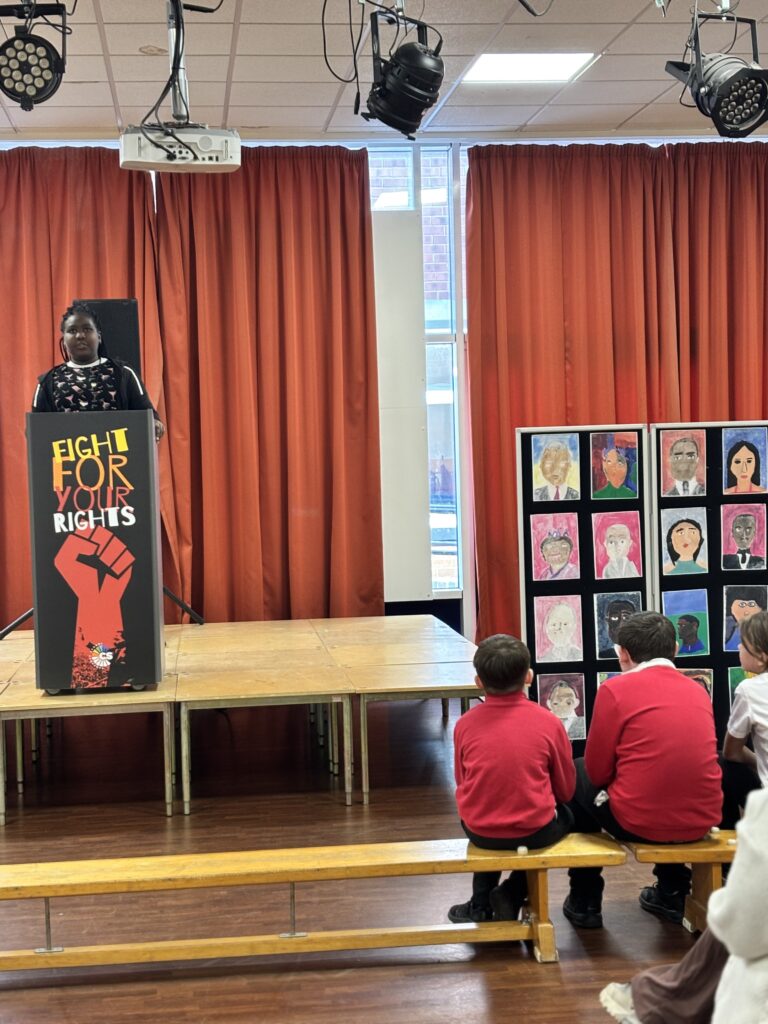
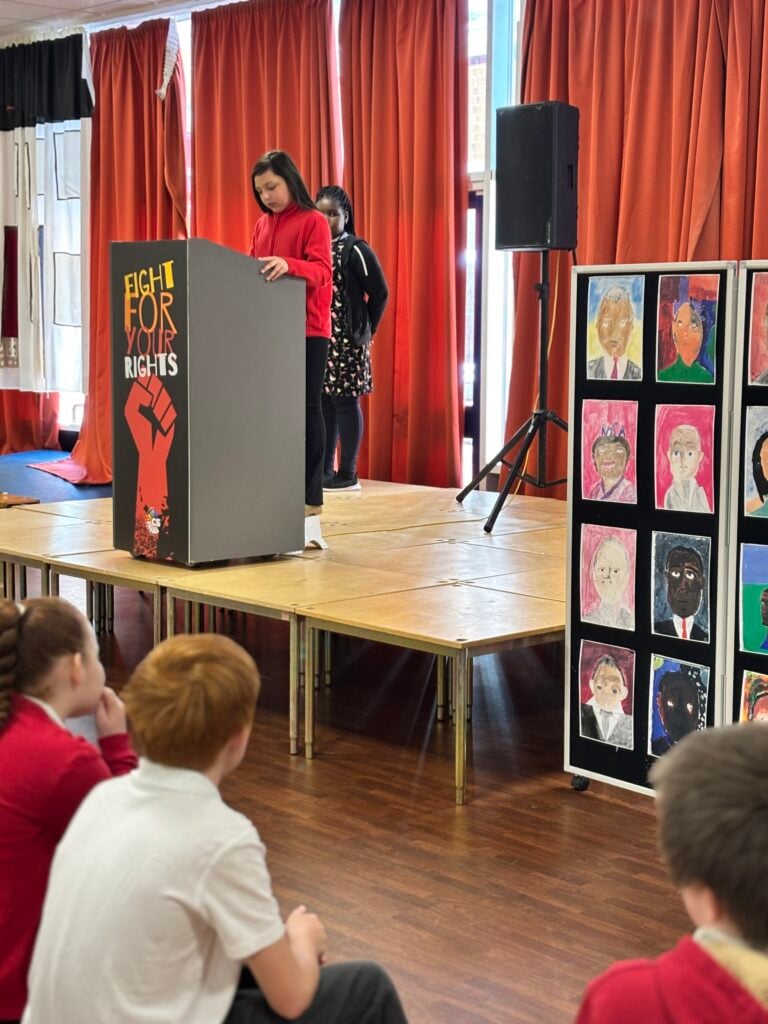
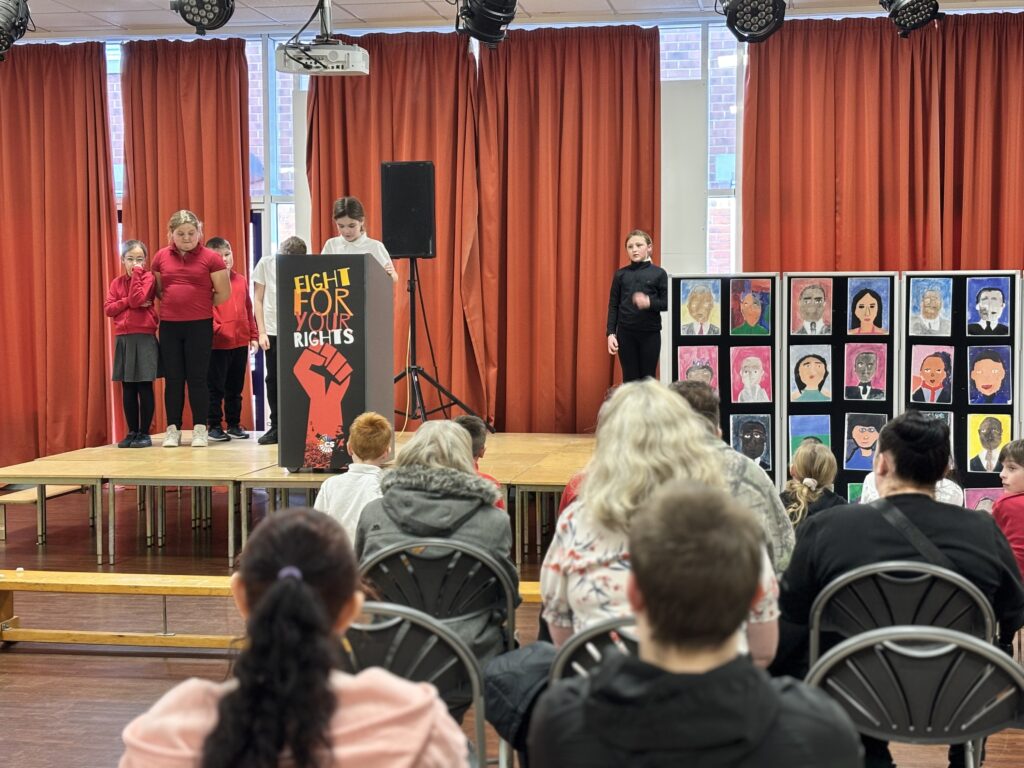
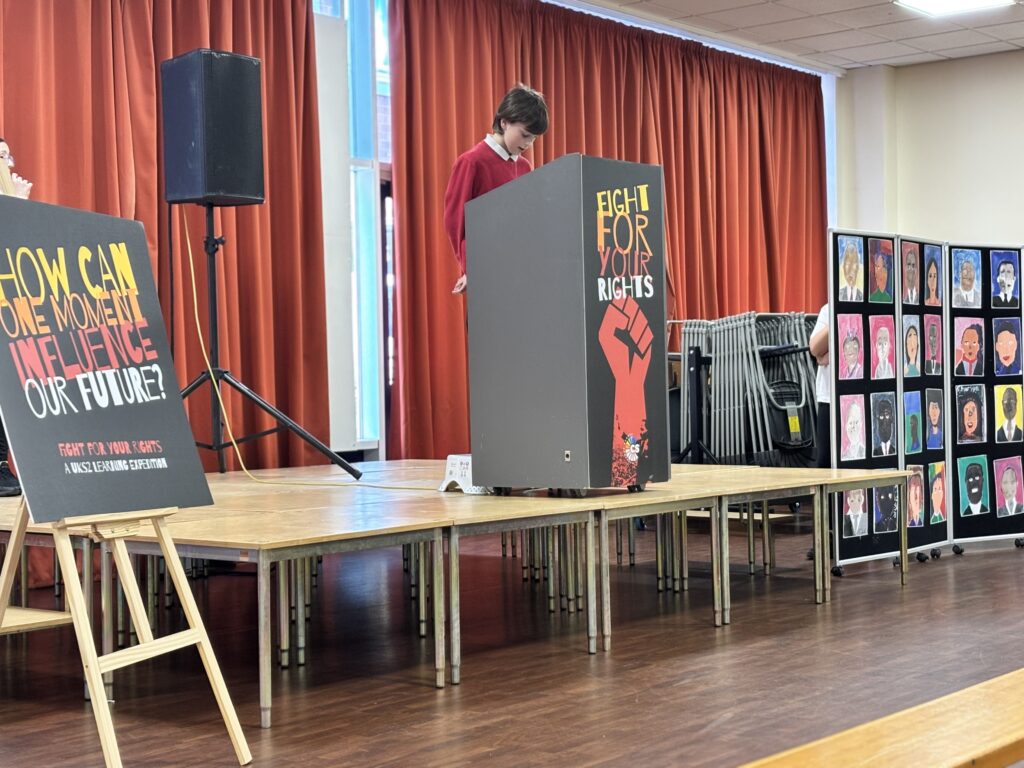
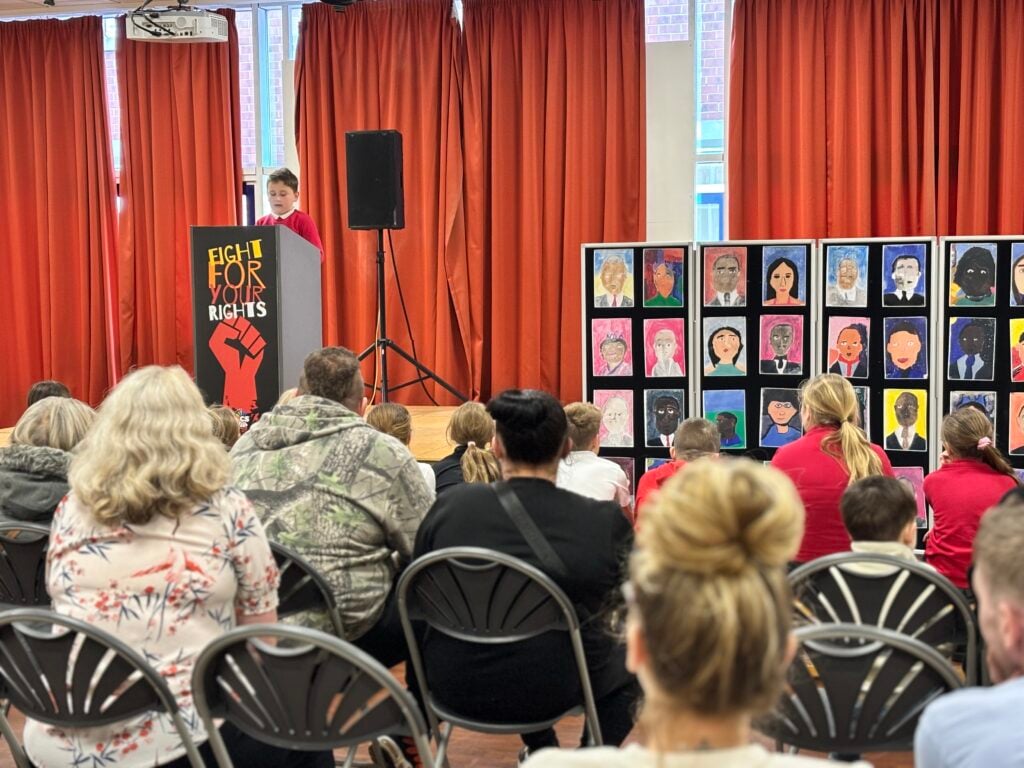
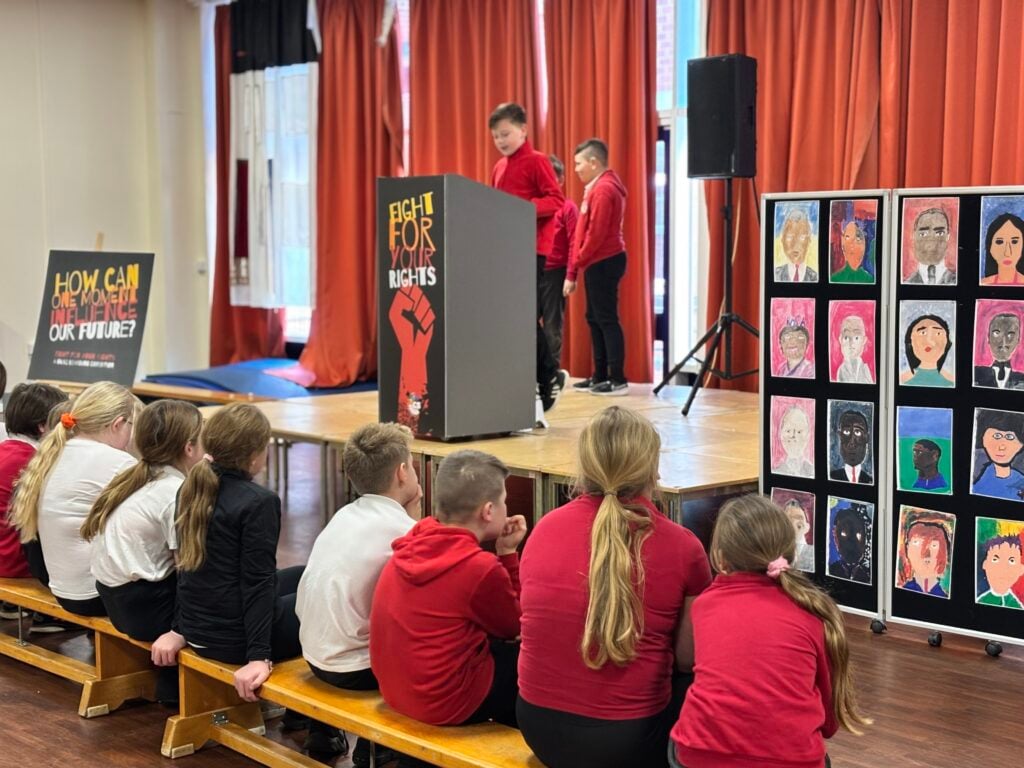
To bring their current expedition to an end, Crew Hamill and Crew Wilkinson took part in their Presentation of Learning this afternoon.
Over the past term, they have been working hard on a series of case studies, with one of the highlights being the powerful words of Martin Luther King Jr. in his iconic “I Have a Dream” speech. As part of this, they have explored the significance of Martin Luther King’s message and its relevance today, not just in the United States but right here in our own community of Doncaster. Inspired by his vision of equality, justice, and hope, each of our students has crafted their own speech, sharing their dreams for a better, brighter future for our city.
Today, they had the opportunity to share these speeches with their families, hopefully inspiring them to also make a difference and support their dreams for Doncaster. Standing proudly on stage, alongside their artwork of inspirational people, inspired by Jonathan Yeo, they gave it their all.
We are so extremely proud of each and every one of them and the effort they have put in to learning their speeches in order to powerfully perform these in front of an audience. The legacy of these speeches will also live on in an article that is being prepared for Doncaster Free Press. Please keep an eye out for this popping up in the near future!











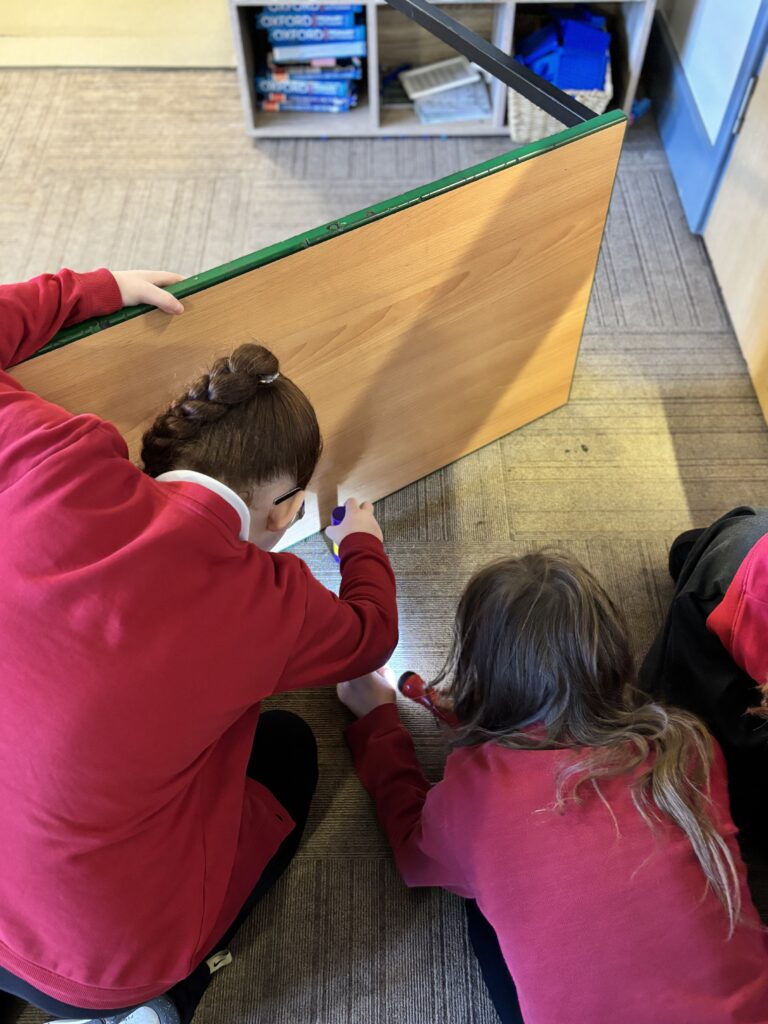
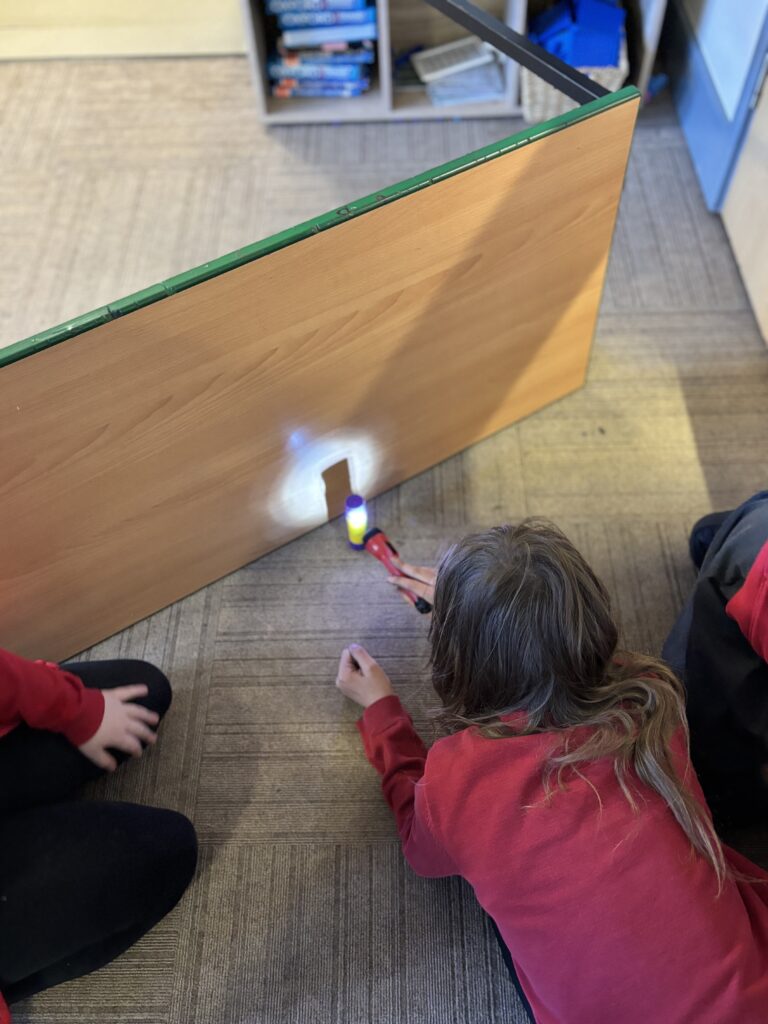
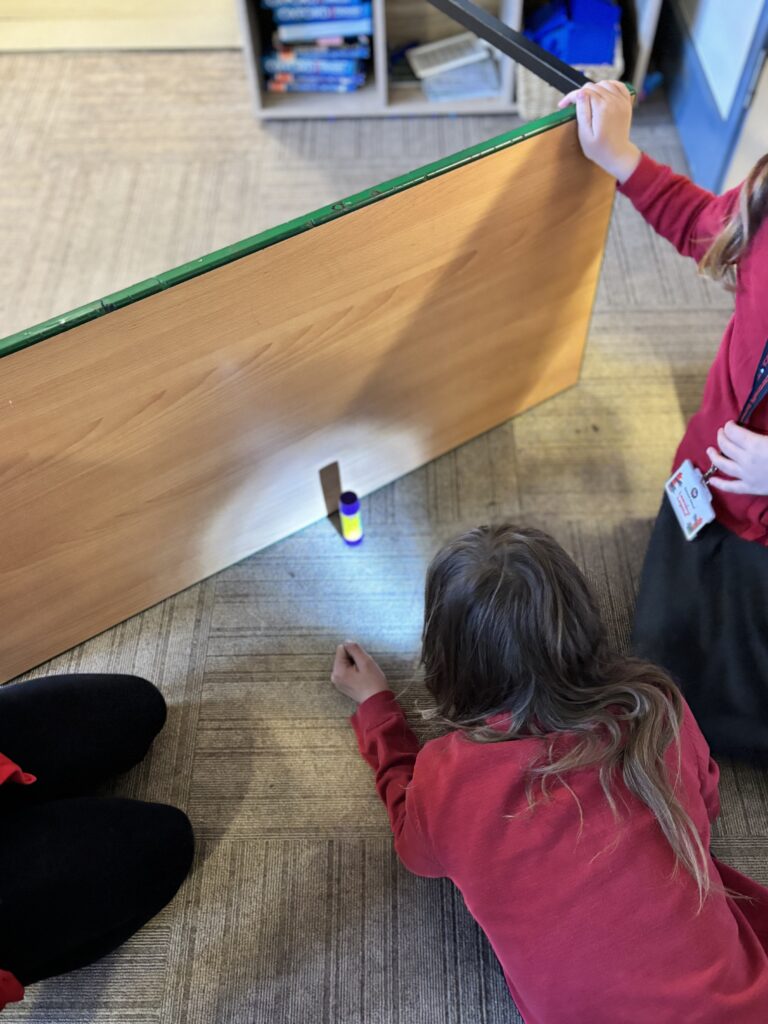
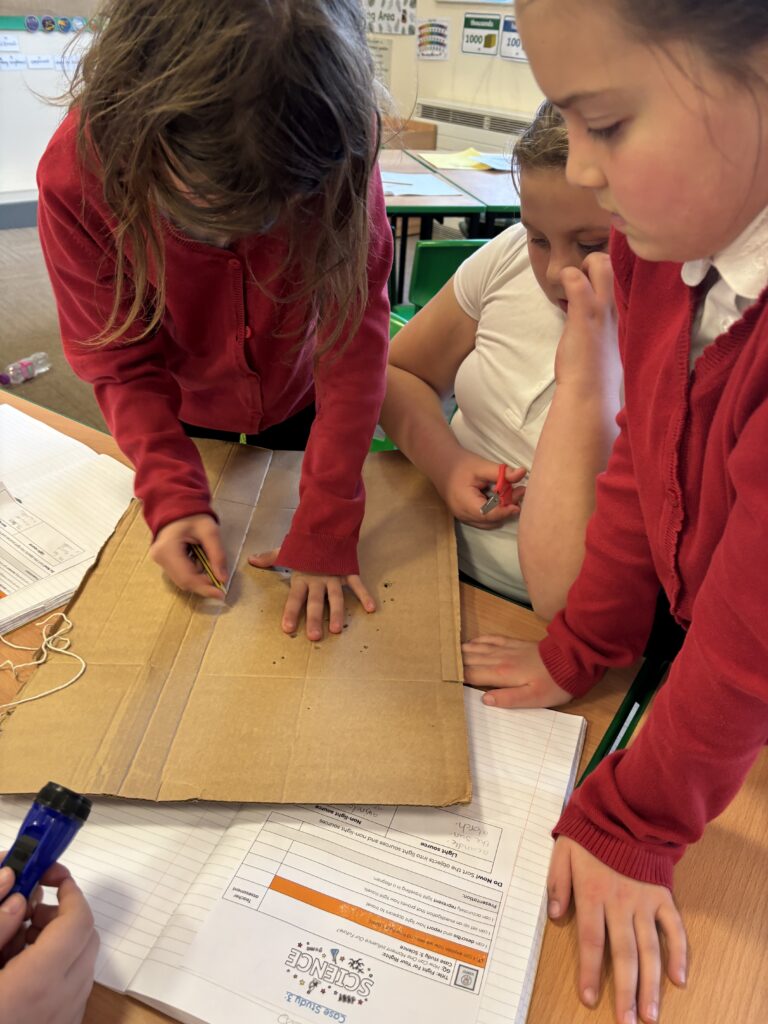
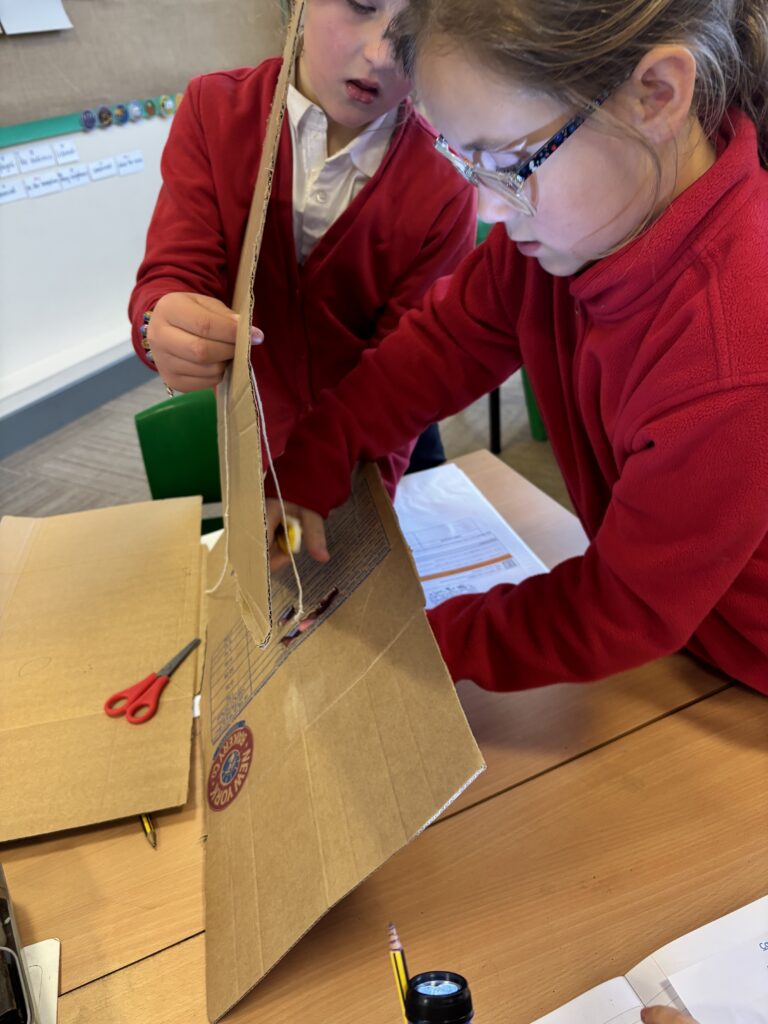
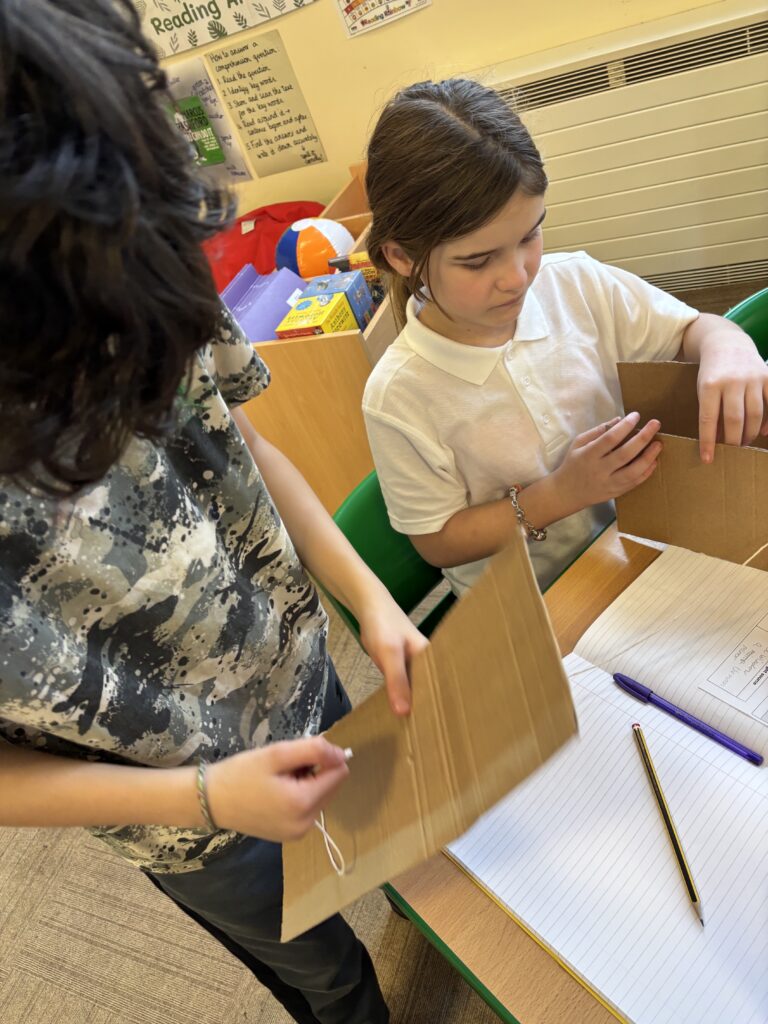
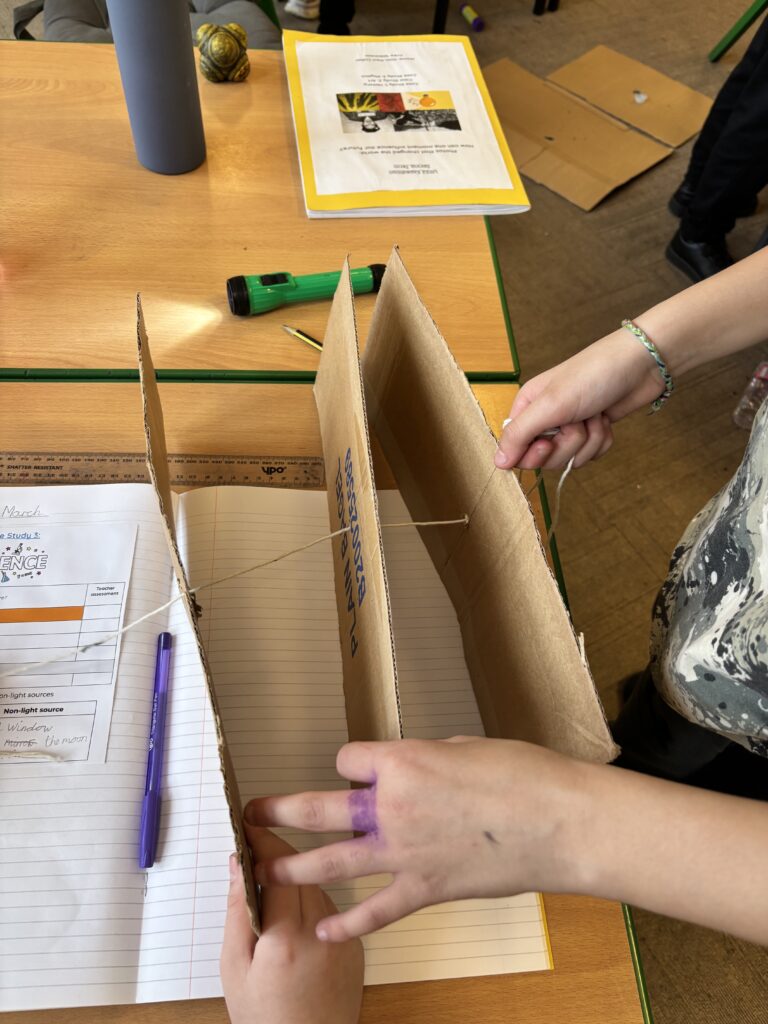
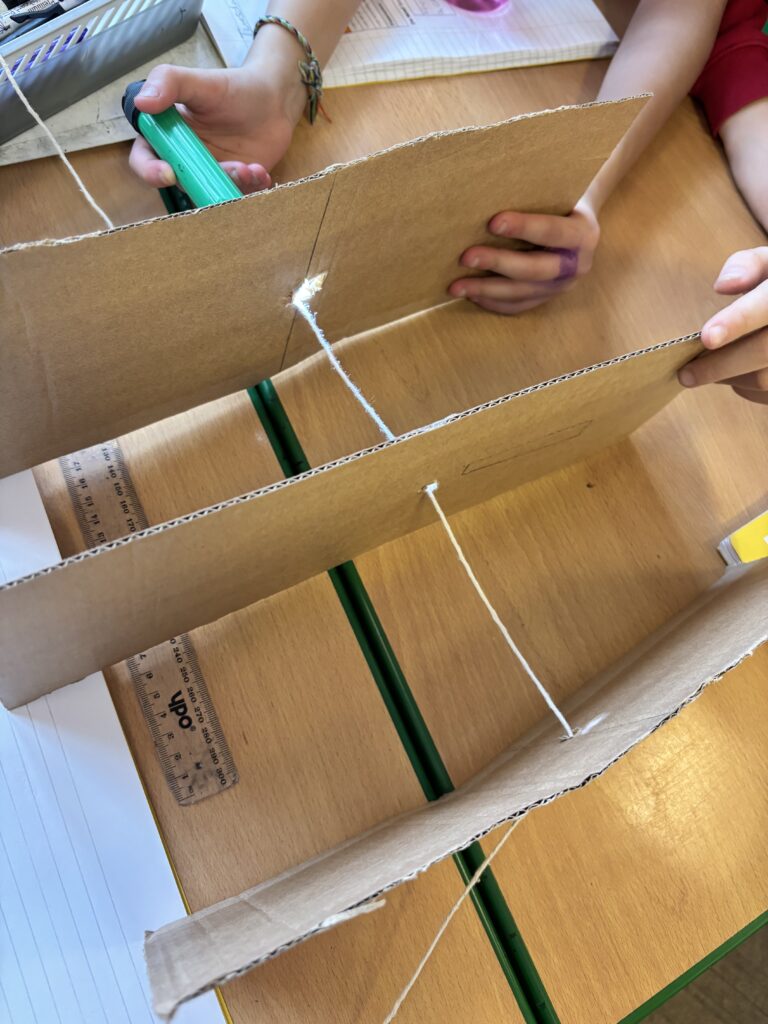
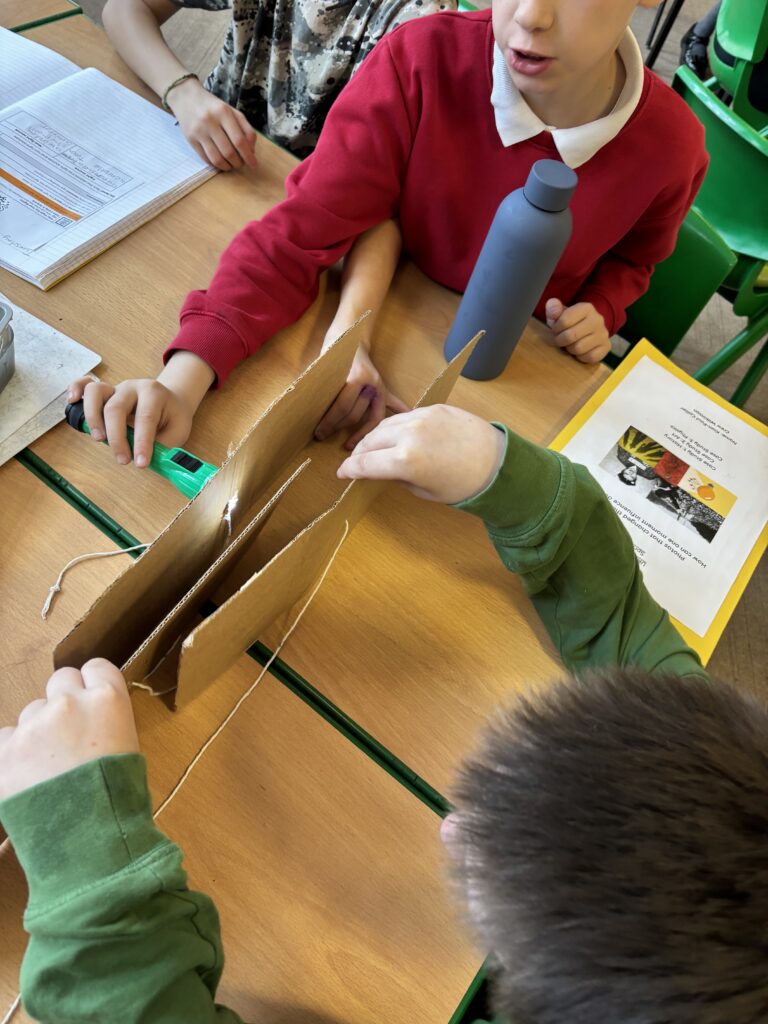
Today, we began investigating how light travels. We worked in mini crews to work with cardboard, string and torches in order to see how the light travelled from one end of the string to the other.






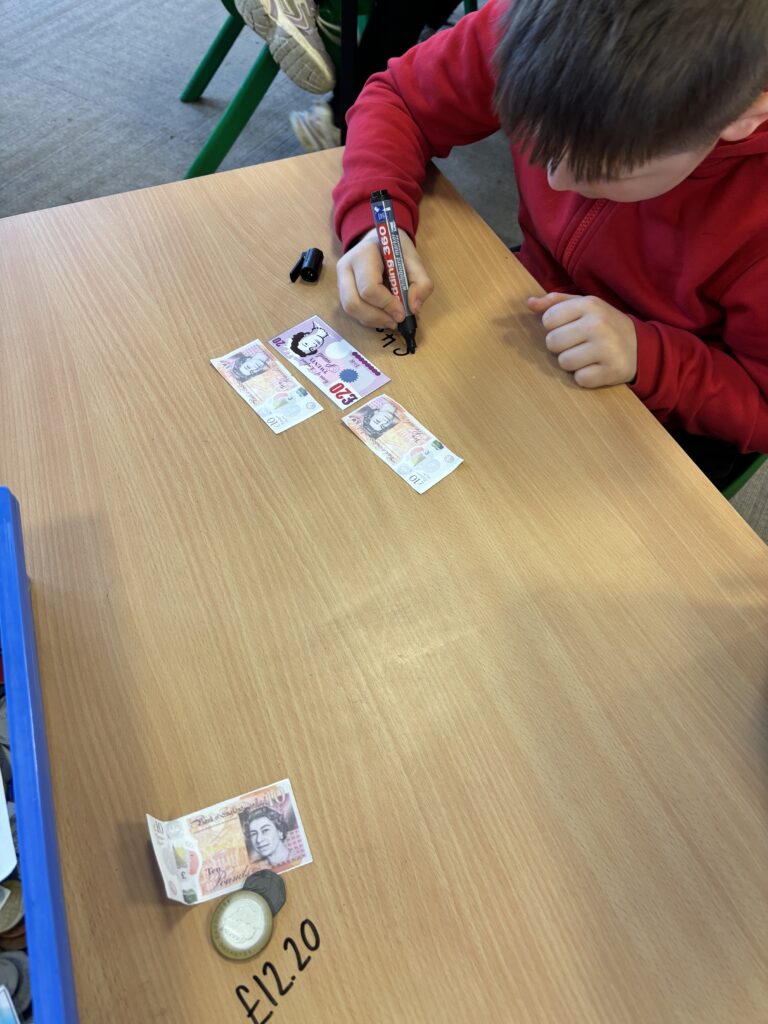
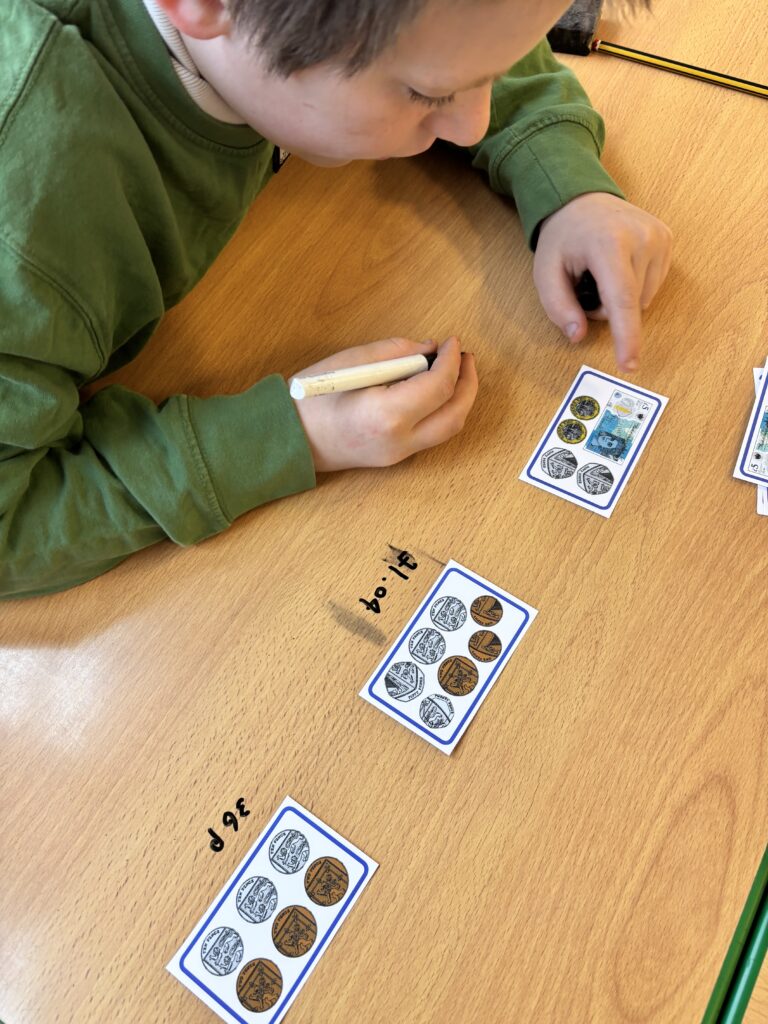
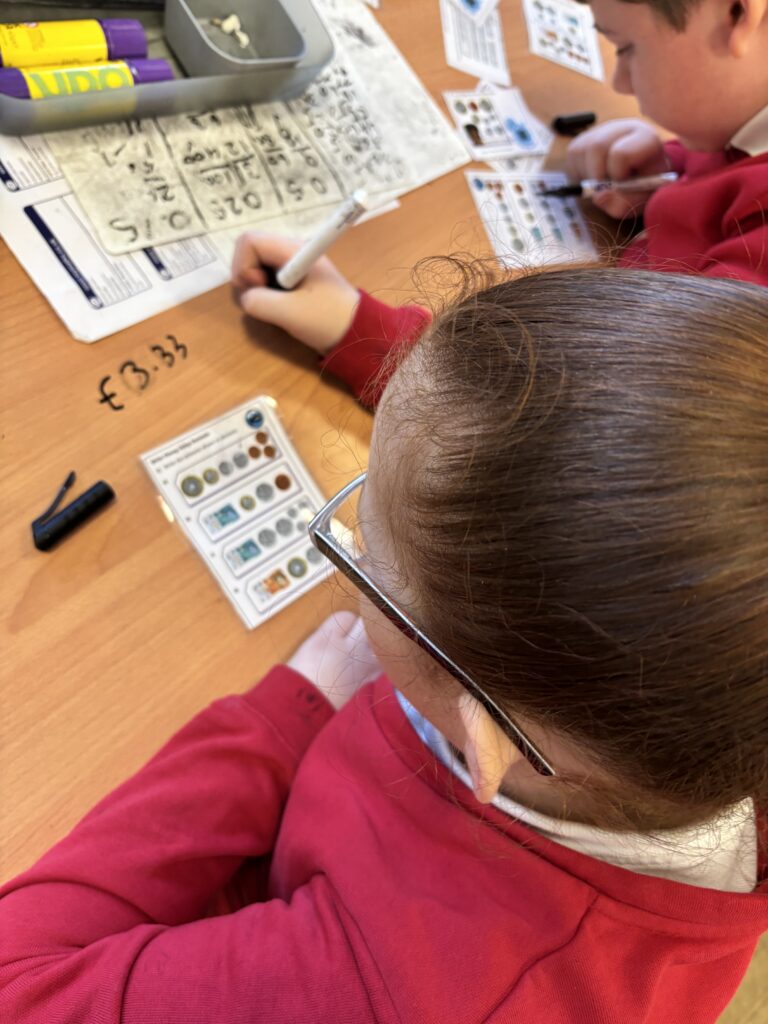
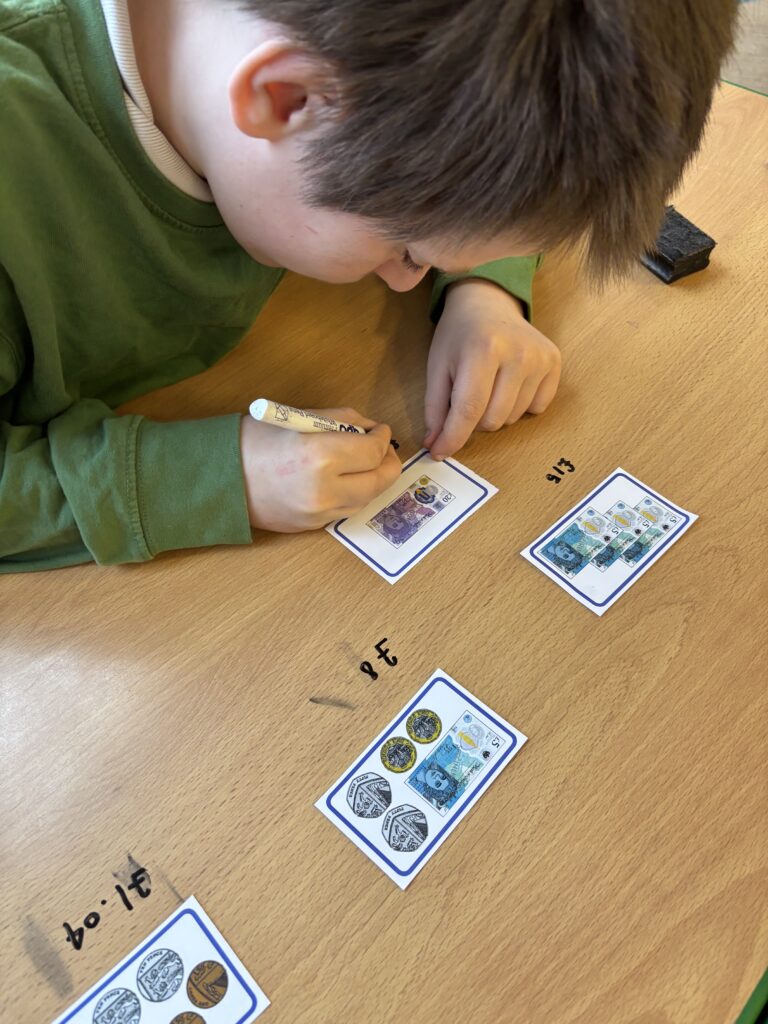
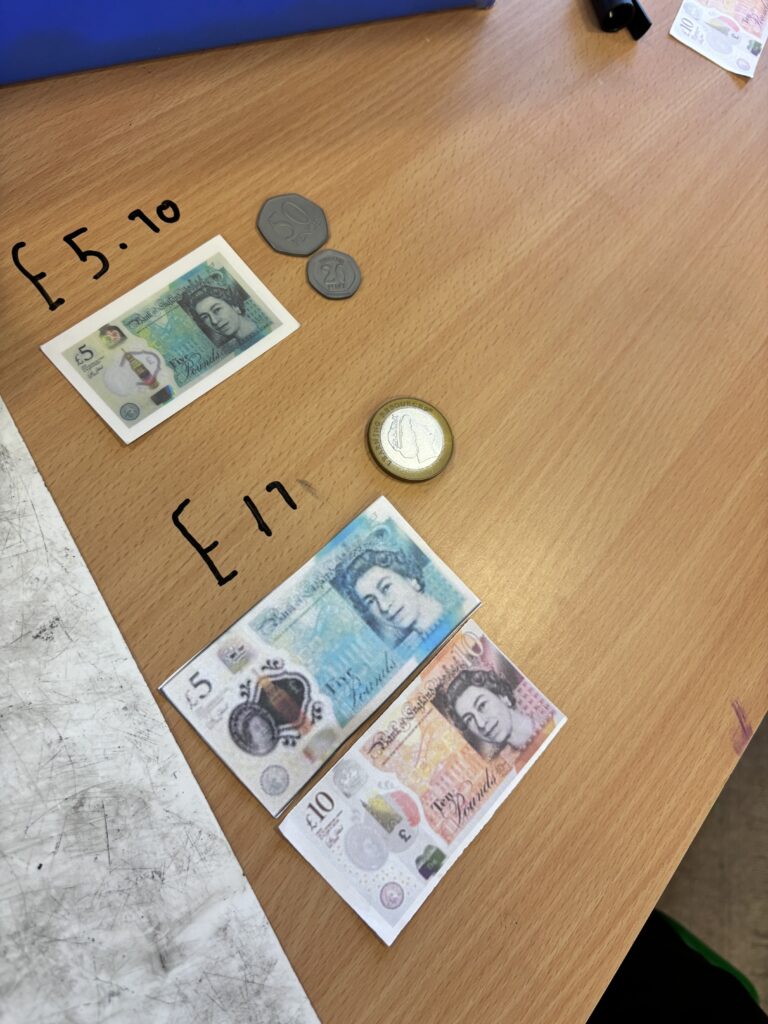
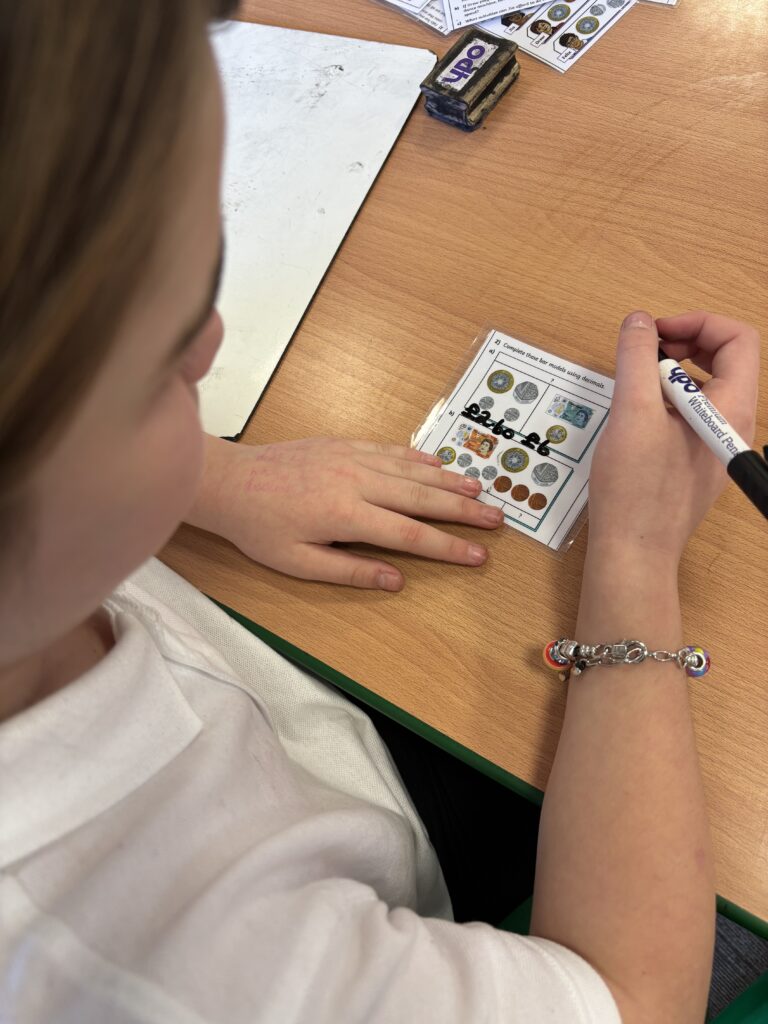
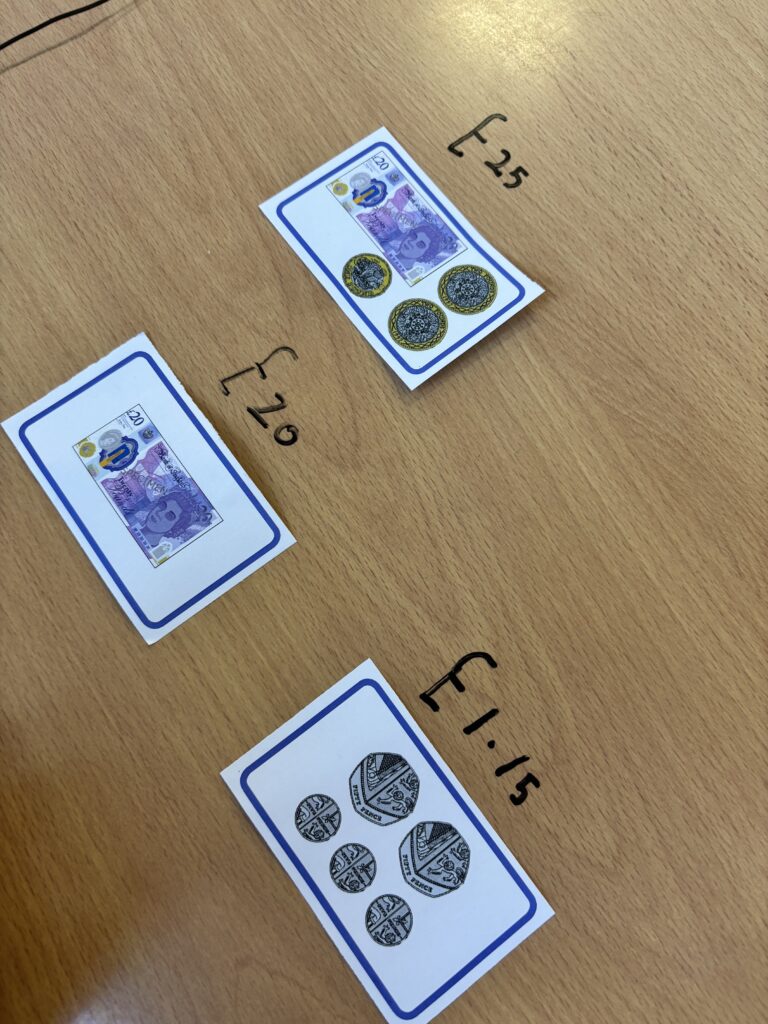
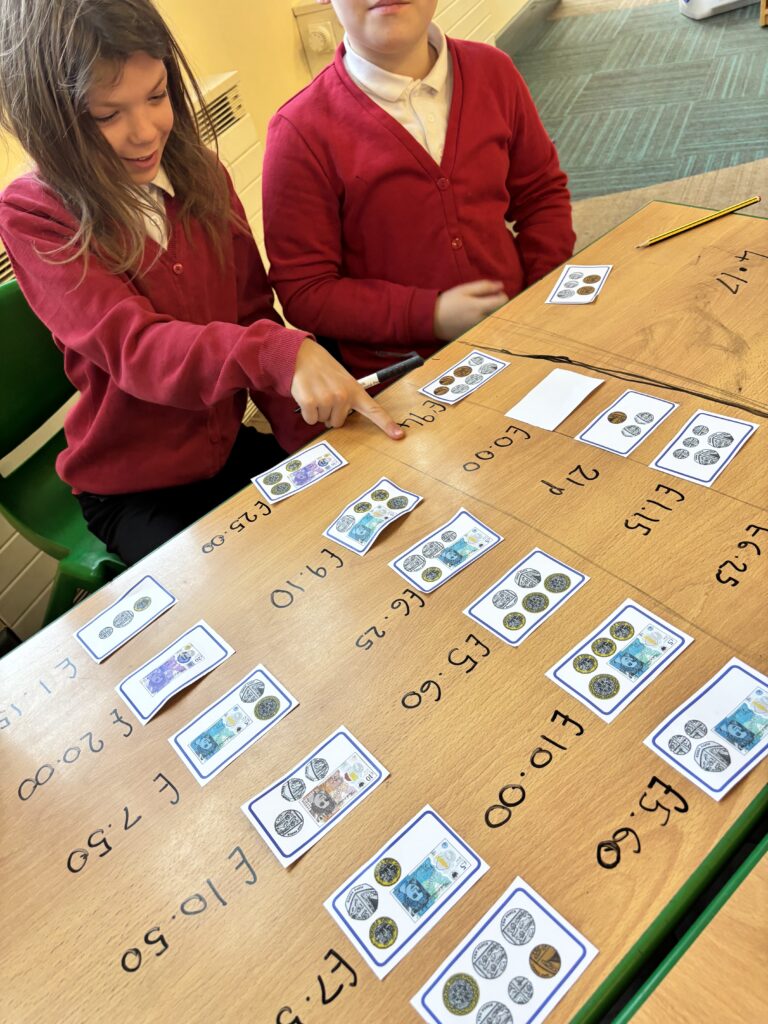
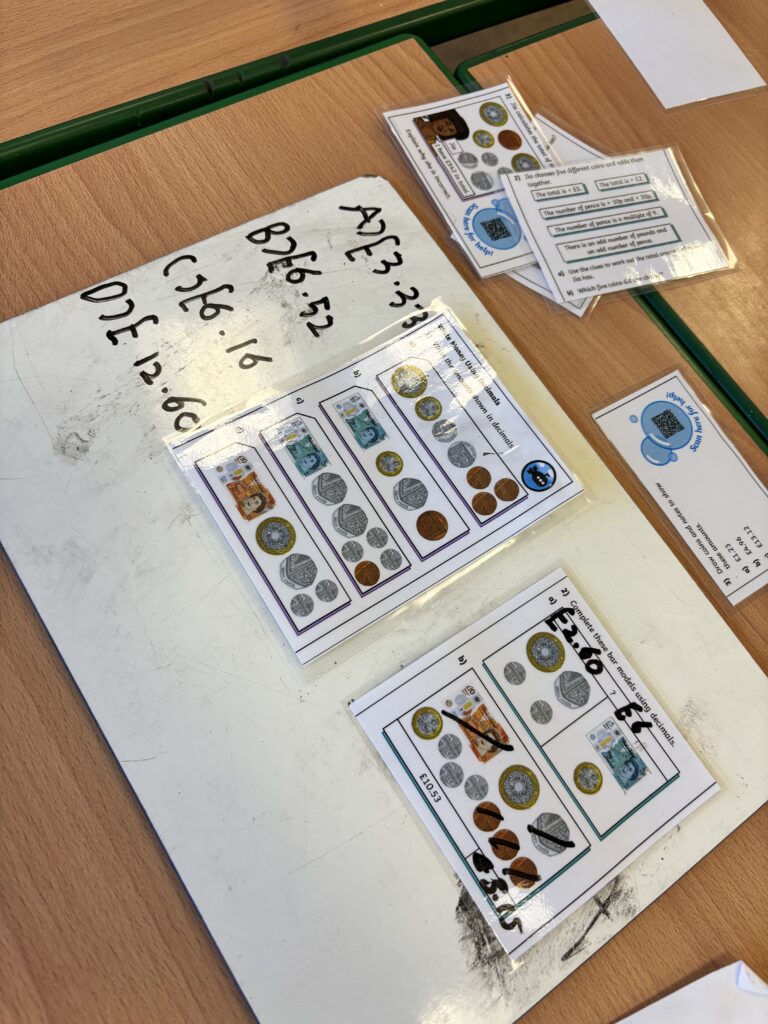
Crew Hamill kick-started their money unit by exploring different amounts of money and ensuring we knew how to write them correctly with a pound sign and decimal point. We took part in a carousel of activities: